A veces, necesitamos verificar el tipo de datos de una variable para calcular datos porque podemos realizar la operación lógica con el mismo tipo de variables. Para verificar el tipo de datos, utilizamos los métodos getClass() y getSimpleName() para obtener la clase y su nombre respectivamente. En esta sección, discutiremos ¿Cómo verificar el tipo de datos en Java?
Implementemos el código para obtener los tipos de datos de las variables. Primero tomamos la información del usuario y luego encontramos el tipo de datos de las variables en las que se almacenará la entrada del usuario.
CheckDataTypeExample.java
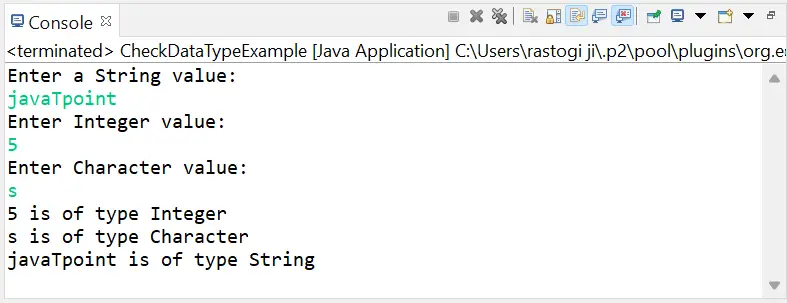
import java.util.*; // create class CheckDataTypeExample to check the datatype of the variable public class CheckDataTypeExample { // main() method start public static void main(String args[]) { // declare variables int intData; char charData; // create Scanner class object to take input from user Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // take input from the user to initialize variables System.out.println('Enter a String value:'); String str = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println('Enter Integer value:'); intData = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println('Enter Character value:'); charData = sc.next().charAt(0); // close Scanner class object sc.close(); // show datatypes of variables by using getClass() and getSimpleName() methods System.out.println(intData + ' is of type ' + ((Object)intData).getClass().getSimpleName()); System.out.println(charData + ' is of type ' + ((Object)charData).getClass().getSimpleName()); System.out.println(str + ' is of type ' + str.getClass().getSimpleName()); } } Producción:
si no en java
Ahora, tenemos un método especial, es decir, obtenerTipo() proporcionado por las clases java.lang.reflect.Field y Character. Entendamos el método getType() de ambas clases una por una.
Campo.getType()
El obtenerTipo() método de el campo La clase se utiliza para obtener el tipo de campo definido por el objeto Campo. El valor de retorno nos ayuda a identificar el tipo de campo.
Sintaxis:
La sintaxis del obtenerTipo() método es el siguiente:
public String getType()
Parámetro: No acepta ningún argumento como parámetro.
Devoluciones: Devuelve un objeto de clase que nos ayuda a identificar el tipo de campo.
Tomemos un ejemplo del método getType() y comprendamos cómo funciona:
GetTypeExample1.java
// import required classes and package if any import java.lang.reflect.Field; // create class GetTypeExample1 to get the type of the Field public class GetTypeExample1 { // main() method start public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //get the name field object by using getField() method Field nameField = Student.class.getField('name'); // use getTyoe() method of the Field to get the type of name field Class value = nameField.getType(); // print the type of name field System.out.println('The type of the name field is ' + value); //get the totalMarks field object by using getField() method Field marksField = Student.class.getField('totalMarks'); // use getTyoe() method of the Field to get the type of totalMarks field value = marksField.getType(); // print the type of name field System.out.println('The type of the totalMarks field is ' + value); //get the totalFees field object by using getField() method Field feesField = Student.class.getField('totalFees'); // use getTyoe() method of the Field to get the type of name field value = feesField.getType(); // print the type of the totalFees field System.out.println('The type of the totalFees field is ' + value); } } // create a simple student class class Student { // declare and initialize variables public static String name = 'John'; public static double totalMarks = 380; public static float totalFees = 3413.99f; // getter for student name public static String getName() { return name; } // setter for student name public static void setName(String stdName) { name = stdName; } // getter for totalMarks public static double getTotalMarks() { return totalMarks; } // setter for totalMarks public static void setMarks(double marks) { totalMarks = marks; } // getter for totalFees public static float getTotalFees() { return totalFees; } // setter for totalFees public static void setFees(float fees) { totalFees = fees; } } Producción:
sonrisa más hermosa

Usando el método Field.getType()
El obtenerTipo() método de Personaje La clase se utiliza para obtener la categoría general del personaje dado. El método getType() viene con dos variaciones basadas en el parámetro, es decir, Carácter.getType(char ch) y Carácter.getType(int codePoint) .
El método getType() que toma char como parámetro no puede manejar caracteres suplementarios, mientras que el método getType() que toma int como parámetro puede manejar caracteres suplementarios.
Sintaxis:
El obtenerTipo() método de la Personaje clase tiene la siguiente sintaxis:
tabla de reacciones
public static int getType(char ch) public static int getType(int codePoint)
Parámetro: La primera variación del método getType() acepta un parámetro de tipo carbonizarse y la segunda variación del método acepta un parámetro de tipo int, es decir, codePoint.
Devoluciones: Ambos métodos devuelven un valor entero que indica la categoría general del carácter.
Tomemos un ejemplo del método getType() y comprendamos cómo funciona:
GetTypeExample2.java
// import required classes and package if any // create class GetTypeExample2 to get the general category of the given character public class GetTypeExample2 { // main() method start public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { // use setter to set ch1, ch2 in CharData CharData.setChar1('C'); CharData.setChar2('%'); // use getter to get char1 and char2 char char1 = CharData.getChar1(); char char2 = CharData.getChar2(); // use getType() method of Character class int val1 = Character.getType(char1); int val2 = Character.getType(char2); // print categories of char1 and char2 System.out.println('The category of ' +char1 + ' is '+ val1); System.out.println('The category of ' +char2 + ' is '+ val2); } } // create a simple CharData class class CharData { // declare variables of type char static char ch1, ch2; // getter for ch1 public static char getChar1() { return ch1; } // setter for ch1 public static void setChar1(char ch) { ch1 = ch; } // getter for ch2 public static char getChar2() { return ch2; } // setter for ch2 public static void setChar2(char ch) { ch2 = ch; } } Producción:

GetTypeExample3.java
// import required classes and package if any import java.lang.reflect.Field; // create class GetTypeExample3 to get the general category of the given character public class GetTypeExample3 { // main() method start public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { // use setter to set code1, code2 in CodePoint CodePoint.setCodePoint1(0x0037); CodePoint.setCodePoint2(0x016f); // use getter to get code1 and code2 int code1 = CodePoint.getCodePoint1(); int code2 = CodePoint.getCodePoint2(); // use getType() method of Character class int val1 = Character.getType(code1); int val2 = Character.getType(code2); // print categories of char1 and char2 System.out.println('The category of ' +code1+ ' is '+ val1); System.out.println('The category of ' +code2+ ' is '+ val2); } } // create a simple CodePoint class class CodePoint { // declare variables of type int static int codePoint1, codePoint2; // getter for codePoint1 public static int getCodePoint1() { return codePoint1; } // setter for codePoint1 public static void setCodePoint1(int code1) { codePoint1 = code1; } // getter for codePoint2 public static int getCodePoint2() { return codePoint2; } // setter for codePoint2 public static void setCodePoint2(int code2) { codePoint2 = code2; } } Producción:

