Dado un
Un árbol de búsqueda binaria
Producción:
Recorrido en orden: 10 20 30 100 150 200 300
Recorrido de reserva: 100 20 10 30 200 150 300
Giro postal transversal: 10 30 20 150 300 200 100
Aporte:
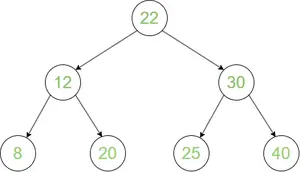
Árbol de búsqueda binaria
Producción:
Recorrido en orden: 8 12 20 22 25 30 40
Recorrido de reserva: 22 12 8 20 30 25 40
Pedido por correo transversal: 8 20 12 25 40 30 22
Recorrido en orden :
A continuación se muestra la idea para resolver el problema:
En la primera travesía subárbol izquierdo luego visita el raíz y luego atravesar el subárbol derecho .
Siga los pasos a continuación para implementar la idea:
- Atravesar el subárbol izquierdo
- Visite la raíz e imprima los datos.
- Atraviesa el subárbol derecho
El recorrido en orden del BST proporciona los valores de los nodos en orden. Para obtener el orden decreciente, visite los subárboles derecho, raíz e izquierdo.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del recorrido en orden.
C++
// C++ code to implement the approach> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Class describing a node of tree> class> Node {> public>:> >int> data;> >Node* left;> >Node* right;> >Node(>int> v)> >{> >this>->datos = v;> >this>->izquierda =>this>->derecha = NULO;> >}> };> // Inorder Traversal> void> printInorder(Node* node)> {> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>;> >// Traverse left subtree> >printInorder(node->izquierda);> >// Visit node> >cout ' '; // Traverse right subtree printInorder(node->bien); } // Código del controlador int main() { // Construye el árbol Node* root = new Node(100); raíz->izquierda = nuevo Nodo(20); raíz->derecha = nuevo Nodo(200); raíz->izquierda->izquierda = nuevo Nodo(10); raíz->izquierda->derecha = nuevo Nodo(30); raíz->derecha->izquierda = nuevo Nodo(150); raíz->derecha->derecha = nuevo Nodo(300); // Llamada a función cout<< 'Inorder Traversal: '; printInorder(root); return 0; }> |
>
>
Java
// Java code to implement the approach> import> java.io.*;> // Class describing a node of tree> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node left;> >Node right;> >Node(>int> v)> >{> >this>.data = v;> >this>.left =>this>.right =>null>;> >}> }> class> GFG {> >// Inorder Traversal> >public> static> void> printInorder(Node node)> >{> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return>;> >// Traverse left subtree> >printInorder(node.left);> >// Visit node> >System.out.print(node.data +>' '>);> >// Traverse right subtree> >printInorder(node.right);> >}> >// Driver Code> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Build the tree> >Node root =>new> Node(>100>);> >root.left =>new> Node(>20>);> >root.right =>new> Node(>200>);> >root.left.left =>new> Node(>10>);> >root.left.right =>new> Node(>30>);> >root.right.left =>new> Node(>150>);> >root.right.right =>new> Node(>300>);> >// Function call> >System.out.print(>'Inorder Traversal: '>);> >printInorder(root);> >}> }> // This code is contributed by Rohit Pradhan> |
>
funciones de cadena en java
>
Python3
# Python3 code to implement the approach> # Class describing a node of tree> class> Node:> >def> __init__(>self>, v):> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> >self>.data>=> v> # Inorder Traversal> def> printInorder(root):> >if> root:> ># Traverse left subtree> >printInorder(root.left)> > ># Visit node> >print>(root.data,end>=>' '>)> > ># Traverse right subtree> >printInorder(root.right)> # Driver code> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> ># Build the tree> >root>=> Node(>100>)> >root.left>=> Node(>20>)> >root.right>=> Node(>200>)> >root.left.left>=> Node(>10>)> >root.left.right>=> Node(>30>)> >root.right.left>=> Node(>150>)> >root.right.right>=> Node(>300>)> ># Function call> >print>(>'Inorder Traversal:'>,end>=>' '>)> >printInorder(root)> ># This code is contributed by ajaymakvana.> |
>
>
C#
// Include namespace system> using> System;> // Class describing a node of tree> public> class> Node> {> >public> int> data;> >public> Node left;> >public> Node right;> >public> Node(>int> v)> >{> >this>.data = v;> >this>.left =>this>.right =>null>;> >}> }> public> class> GFG> {> >// Inorder Traversal> >public> static> void> printInorder(Node node)> >{> >if> (node ==>null>)> >{> >return>;> >}> >// Traverse left subtree> >GFG.printInorder(node.left);> >// Visit node> >Console.Write(node.data.ToString() +>' '>);> >// Traverse right subtree> >GFG.printInorder(node.right);> >}> >// Driver Code> >public> static> void> Main(String[] args)> >{> >// Build the tree> >var> root =>new> Node(100);> >root.left =>new> Node(20);> >root.right =>new> Node(200);> >root.left.left =>new> Node(10);> >root.left.right =>new> Node(30);> >root.right.left =>new> Node(150);> >root.right.right =>new> Node(300);> >// Function call> >Console.Write(>'Inorder Traversal: '>);> >GFG.printInorder(root);> >}> }> |
>
>
JavaScript
// JavaScript code to implement the approach> class Node {> constructor(v) {> this>.left =>null>;> this>.right =>null>;> this>.data = v;> }> }> // Inorder Traversal> function> printInorder(root)> {> if> (root)> {> // Traverse left subtree> printInorder(root.left);> // Visit node> console.log(root.data);> // Traverse right subtree> printInorder(root.right);> }> }> // Driver code> if> (>true>)> {> // Build the tree> let root =>new> Node(100);> root.left =>new> Node(20);> root.right =>new> Node(200);> root.left.left =>new> Node(10);> root.left.right =>new> Node(30);> root.right.left =>new> Node(150);> root.right.right =>new> Node(300);> // Function call> console.log(>'Inorder Traversal:'>);> printInorder(root);> }> // This code is contributed by akashish__> |
>
>Producción
Inorder Traversal: 10 20 30 100 150 200 300>
Complejidad del tiempo: O (N), donde N es el número de nodos.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(h), donde h es la altura del árbol
Recorrido de pedidos anticipados:
A continuación se muestra la idea para resolver el problema:
En primera visita el raíz luego atravesar subárbol izquierdo y luego atravesar el subárbol derecho .
Siga los pasos a continuación para implementar la idea:
- Visite la raíz e imprima los datos.
- Atravesar el subárbol izquierdo
- Atraviesa el subárbol derecho
A continuación se muestra la implementación del recorrido de preorden.
C++
// C++ code to implement the approach> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Class describing a node of tree> class> Node {> public>:> >int> data;> >Node* left;> >Node* right;> >Node(>int> v)> >{> >this>->datos = v;> >this>->izquierda =>this>->derecha = NULO;> >}> };> // Preorder Traversal> void> printPreOrder(Node* node)> {> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>;> >// Visit Node> >cout ' '; // Traverse left subtree printPreOrder(node->izquierda); // Atravesar el subárbol derecho printPreOrder(nodo->derecha); } // Código del controlador int main() { // Construye el árbol Node* root = new Node(100); raíz->izquierda = nuevo Nodo(20); raíz->derecha = nuevo Nodo(200); raíz->izquierda->izquierda = nuevo Nodo(10); raíz->izquierda->derecha = nuevo Nodo(30); raíz->derecha->izquierda = nuevo Nodo(150); raíz->derecha->derecha = nuevo Nodo(300); // Llamada a función cout<< 'Preorder Traversal: '; printPreOrder(root); return 0; }> |
>
>
Java
// Java code to implement the approach> import> java.io.*;> // Class describing a node of tree> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node left;> >Node right;> >Node(>int> v)> >{> >this>.data = v;> >this>.left =>this>.right =>null>;> >}> }> class> GFG {> >// Preorder Traversal> >public> static> void> printPreorder(Node node)> >{> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return>;> >// Visit node> >System.out.print(node.data +>' '>);> >// Traverse left subtree> >printPreorder(node.left);> >// Traverse right subtree> >printPreorder(node.right);> >}> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Build the tree> >Node root =>new> Node(>100>);> >root.left =>new> Node(>20>);> >root.right =>new> Node(>200>);> >root.left.left =>new> Node(>10>);> >root.left.right =>new> Node(>30>);> >root.right.left =>new> Node(>150>);> >root.right.right =>new> Node(>300>);> >// Function call> >System.out.print(>'Preorder Traversal: '>);> >printPreorder(root);> >}> }> // This code is contributed by lokeshmvs21.> |
>
>
Python3
class> Node:> >def> __init__(>self>, v):> >self>.data>=> v> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> # Preorder Traversal> def> printPreOrder(node):> >if> node>is> None>:> >return> ># Visit Node> >print>(node.data, end>=> ' '>)> ># Traverse left subtree> >printPreOrder(node.left)> ># Traverse right subtree> >printPreOrder(node.right)> # Driver code> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> ># Build the tree> >root>=> Node(>100>)> >root.left>=> Node(>20>)> >root.right>=> Node(>200>)> >root.left.left>=> Node(>10>)> >root.left.right>=> Node(>30>)> >root.right.left>=> Node(>150>)> >root.right.right>=> Node(>300>)> ># Function call> >print>(>'Preorder Traversal: '>, end>=> '')> >printPreOrder(root)> |
>
>
C#
// Include namespace system> using> System;> // Class describing a node of tree> public> class> Node> {> >public> int> data;> >public> Node left;> >public> Node right;> >public> Node(>int> v)> >{> >this>.data = v;> >this>.left =>this>.right =>null>;> >}> }> public> class> GFG> {> >// Preorder Traversal> >public> static> void> printPreorder(Node node)> >{> >if> (node ==>null>)> >{> >return>;> >}> >// Visit node> >Console.Write(node.data.ToString() +>' '>);> >// Traverse left subtree> >GFG.printPreorder(node.left);> >// Traverse right subtree> >GFG.printPreorder(node.right);> >}> >public> static> void> Main(String[] args)> >{> >// Build the tree> >var> root =>new> Node(100);> >root.left =>new> Node(20);> >root.right =>new> Node(200);> >root.left.left =>new> Node(10);> >root.left.right =>new> Node(30);> >root.right.left =>new> Node(150);> >root.right.right =>new> Node(300);> >// Function call> >Console.Write(>'Preorder Traversal: '>);> >GFG.printPreorder(root);> >}> }> |
>
diferencia entre matriz y lista de matrices
>
JavaScript
class Node {> >constructor(v) {> >this>.data = v;> >this>.left =>this>.right =>null>;> >}> }> function> printPreOrder(node) {> >if> (node ==>null>)>return>;> >console.log(node.data +>' '>);> >printPreOrder(node.left);> >printPreOrder(node.right);> }> // Build the tree> let root =>new> Node(100);> root.left =>new> Node(20);> root.right =>new> Node(200);> root.left.left =>new> Node(10);> root.left.right =>new> Node(30);> root.right.left =>new> Node(150);> root.right.right =>new> Node(300);> console.log(>'Preorder Traversal: '>);> printPreOrder(root);> // This code is contributed by akashish__> |
>
>Producción
Preorder Traversal: 100 20 10 30 200 150 300>
Complejidad del tiempo: O (N), donde N es el número de nodos.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(H), donde H es la altura del árbol
Recorrido de giro postal:
A continuación se muestra la idea para resolver el problema:
En la primera travesía subárbol izquierdo luego atraviesa el subárbol derecho y luego visitar el raíz .
Siga los pasos a continuación para implementar la idea:
- Atravesar el subárbol izquierdo
- Atraviesa el subárbol derecho
- Visite la raíz e imprima los datos.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del recorrido posterior al pedido:
C++
// C++ code to implement the approach> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Class to define structure of a node> class> Node {> public>:> >int> data;> >Node* left;> >Node* right;> >Node(>int> v)> >{> >this>->datos = v;> >this>->izquierda =>this>->derecha = NULO;> >}> };> // PostOrder Traversal> void> printPostOrder(Node* node)> {> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>;> >// Traverse left subtree> >printPostOrder(node->izquierda);> >// Traverse right subtree> >printPostOrder(node->derecha);> >// Visit node> >cout ' '; } // Driver code int main() { Node* root = new Node(100); root->izquierda = nuevo Nodo(20); raíz->derecha = nuevo Nodo(200); raíz->izquierda->izquierda = nuevo Nodo(10); raíz->izquierda->derecha = nuevo Nodo(30); raíz->derecha->izquierda = nuevo Nodo(150); raíz->derecha->derecha = nuevo Nodo(300); // Llamada a función cout<< 'PostOrder Traversal: '; printPostOrder(root); cout << '
'; return 0; }> |
>
>
Java
// Java code to implement the approach> import> java.io.*;> // Class describing a node of tree> class> GFG {> > >static> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node left;> >Node right;> >Node(>int> v)> >{> >this>.data = v;> >this>.left =>this>.right =>null>;> >}> }> >// Preorder Traversal> >public> static> void> printPreorder(Node node)> >{> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return>;> >// Traverse left subtree> >printPreorder(node.left);> >// Traverse right subtree> >printPreorder(node.right);> > >// Visit node> >System.out.print(node.data +>' '>);> >}> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Build the tree> >Node root =>new> Node(>100>);> >root.left =>new> Node(>20>);> >root.right =>new> Node(>200>);> >root.left.left =>new> Node(>10>);> >root.left.right =>new> Node(>30>);> >root.right.left =>new> Node(>150>);> >root.right.right =>new> Node(>300>);> >// Function call> >System.out.print(>'Preorder Traversal: '>);> >printPreorder(root);> >}> }> |
>
>
C#
// Include namespace system> using> System;> // Class describing a node of tree> public> class> Node> {> >public> int> data;> >public> Node left;> >public> Node right;> >public> Node(>int> v)> >{> >this>.data = v;> >this>.left =>this>.right =>null>;> >}> }> public> class> GFG> {> >// Preorder Traversal> >public> static> void> printPreorder(Node node)> >{> >if> (node ==>null>)> >{> >return>;> >}> >// Traverse left subtree> >GFG.printPreorder(node.left);> >// Traverse right subtree> >GFG.printPreorder(node.right);> >// Visit node> >Console.Write(node.data.ToString() +>' '>);> >}> >public> static> void> Main(String[] args)> >{> >// Build the tree> >var> root =>new> Node(100);> >root.left =>new> Node(20);> >root.right =>new> Node(200);> >root.left.left =>new> Node(10);> >root.left.right =>new> Node(30);> >root.right.left =>new> Node(150);> >root.right.right =>new> Node(300);> >// Function call> >Console.Write(>'Preorder Traversal: '>);> >GFG.printPreorder(root);> >}> }> |
>
>
Python3
class> Node:> >def> __init__(>self>, v):> >self>.data>=> v> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> # Preorder Traversal> def> printPostOrder(node):> >if> node>is> None>:> >return> ># Traverse left subtree> >printPostOrder(node.left)> ># Traverse right subtree> >printPostOrder(node.right)> > ># Visit Node> >print>(node.data, end>=> ' '>)> # Driver code> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> ># Build the tree> >root>=> Node(>100>)> >root.left>=> Node(>20>)> >root.right>=> Node(>200>)> >root.left.left>=> Node(>10>)> >root.left.right>=> Node(>30>)> >root.right.left>=> Node(>150>)> >root.right.right>=> Node(>300>)> ># Function call> >print>(>'Postorder Traversal: '>, end>=> '')> >printPostOrder(root)> |
>
>
JavaScript
class Node {> >constructor(v) {> >this>.data = v;> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >}> }> // Preorder Traversal> function> printPostOrder(node) {> >if> (node ===>null>) {> >return>;> >}> >// Traverse left subtree> >printPostOrder(node.left);> >// Traverse right subtree> >printPostOrder(node.right);> >// Visit Node> >console.log(node.data, end =>' '>);> }> // Driver code> // Build the tree> let root =>new> Node(100);> root.left =>new> Node(20);> root.right =>new> Node(200);> root.left.left =>new> Node(10);> root.left.right =>new> Node(30);> root.right.left =>new> Node(150);> root.right.right =>new> Node(300);> // Function call> console.log(>'Postorder Traversal: '>, end =>''>);> printPostOrder(root);> // This code is contributed by akashish__> |
>
>Producción
PostOrder Traversal: 10 30 20 150 300 200 100>
Complejidad del tiempo: O (N), donde N es el número de nodos.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(H), donde H es la altura del árbol
