Dado un hora estándar del este , la tarea es buscar un nodo en este hora estándar del este .
Para buscar un valor en BST, considérelo como una matriz ordenada. Ahora podemos realizar fácilmente la operación de búsqueda en BST usando Algoritmo de búsqueda binaria .
Algoritmo para buscar una clave en un árbol de búsqueda binaria determinado:
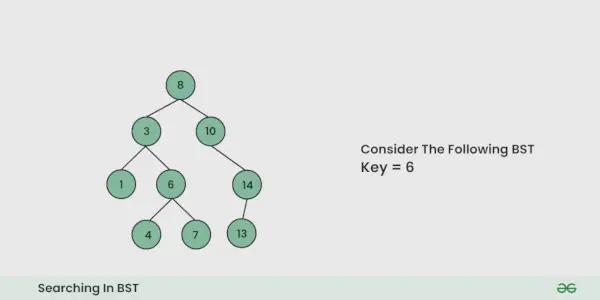
Digamos que queremos buscar el número. X, Empezamos por la raíz. Entonces:
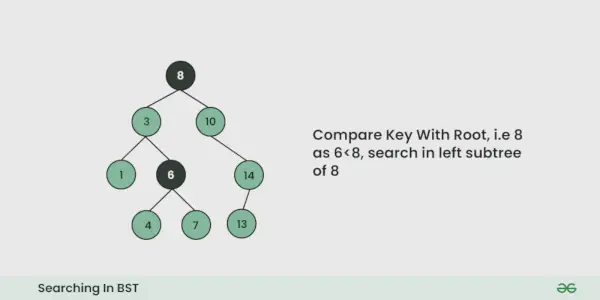
- Comparamos el valor a buscar con el valor de la raíz.
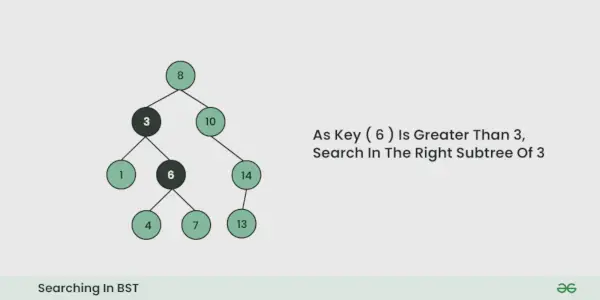
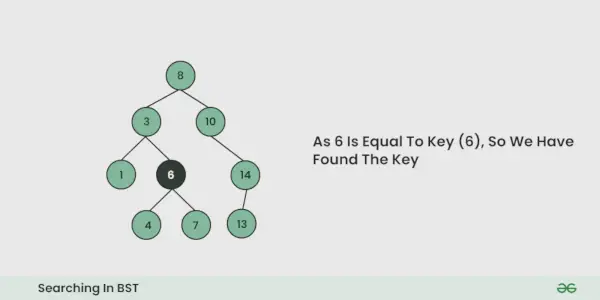
- Si es igual, hemos terminado con la búsqueda, si es más pequeño, sabemos que debemos ir al subárbol izquierdo porque en un árbol de búsqueda binario todos los elementos en el subárbol izquierdo son más pequeños y todos los elementos en el subárbol derecho son más grandes.
- Repita el paso anterior hasta que no sea posible realizar más recorridos.
- Si en cualquier iteración se encuentra la clave, devuelve True. De lo contrario Falso.
Ilustración de la búsqueda en un BST:
Vea la siguiente ilustración para una mejor comprensión:
Práctica recomendadaBuscar un nodo en BST ¡Pruébalo!
Programa para implementar la búsqueda en BST:
C++
// C++ function to search a given key in a given BST> #include> using> namespace> std;> struct> node {> >int> key;> >struct> node *left, *right;> };> // A utility function to create a new BST node> struct> node* newNode(>int> item)> {> >struct> node* temp> >=>new> struct> node;> >temp->clave = elemento;> >temp->izquierda = temp->derecha = NULL;> >return> temp;> }> // A utility function to insert> // a new node with given key in BST> struct> node* insert(>struct> node* node,>int> key)> {> >// If the tree is empty, return a new node> >if> (node == NULL)> >return> newNode(key);> >// Otherwise, recur down the tree> >if> (key key)> >node->izquierda = insertar(nodo->izquierda, clave);> >else> if> (key>nodo->clave)> >node->derecha = insertar(nodo->derecha, clave);> >// Return the (unchanged) node pointer> >return> node;> }> // Utility function to search a key in a BST> struct> node* search(>struct> node* root,>int> key)> > >// Base Cases: root is null or key is present at root> >if> (root == NULL> // Driver Code> int> main()> {> >struct> node* root = NULL;> >root = insert(root, 50);> >insert(root, 30);> >insert(root, 20);> >insert(root, 40);> >insert(root, 70);> >insert(root, 60);> >insert(root, 80);> >// Key to be found> >int> key = 6;> >// Searching in a BST> >if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> >cout << key <<>' not found'> << endl;> >else> >cout << key <<>' found'> << endl;> >key = 60;> >// Searching in a BST> >if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> >cout << key <<>' not found'> << endl;> >else> >cout << key <<>' found'> << endl;> >return> 0;> }> |
>
cadena reemplaza todo java
>
C
// C function to search a given key in a given BST> #include> #include> struct> node {> >int> key;> >struct> node *left, *right;> };> // A utility function to create a new BST node> struct> node* newNode(>int> item)> {> >struct> node* temp> >= (>struct> node*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> node));> >temp->clave = elemento;> >temp->izquierda = temp->derecha = NULL;> >return> temp;> }> // A utility function to insert> // a new node with given key in BST> struct> node* insert(>struct> node* node,>int> key)> {> >// If the tree is empty, return a new node> >if> (node == NULL)> >return> newNode(key);> >// Otherwise, recur down the tree> >if> (key key)> >node->izquierda = insertar(nodo->izquierda, clave);> >else> if> (key>nodo->clave)> >node->derecha = insertar(nodo->derecha, clave);> >// Return the (unchanged) node pointer> >return> node;> }> // Utility function to search a key in a BST> struct> node* search(>struct> node* root,>int> key)> > // Driver Code> int> main()> {> >struct> node* root = NULL;> >root = insert(root, 50);> >insert(root, 30);> >insert(root, 20);> >insert(root, 40);> >insert(root, 70);> >insert(root, 60);> >insert(root, 80);> >// Key to be found> >int> key = 6;> >// Searching in a BST> >if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> >printf>(>'%d not found
'>, key);> >else> >printf>(>'%d found
'>, key);> >key = 60;> >// Searching in a BST> >if> (search(root, key) == NULL)> >printf>(>'%d not found
'>, key);> >else> >printf>(>'%d found
'>, key);> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Java
// Java program to search a given key in a given BST> class> Node {> >int> key;> >Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> item) {> >key = item;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> class> BinarySearchTree {> >Node root;> >// Constructor> >BinarySearchTree() {> >root =>null>;> >}> >// A utility function to insert> >// a new node with given key in BST> >Node insert(Node node,>int> key) {> >// If the tree is empty, return a new node> >if> (node ==>null>) {> >node =>new> Node(key);> >return> node;> >}> >// Otherwise, recur down the tree> >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>nodo.clave) nodo.derecha = insertar(nodo.derecha, clave); // Devuelve el puntero del nodo (sin cambios) return node; } // Función de utilidad para buscar una clave en una búsqueda de nodo BST (raíz de nodo, clave int) // Código de controlador public static void main(String[] args) { BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree(); // Insertando nodos tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); árbol.insertar(árbol.raíz, 30); árbol.insertar(árbol.raíz, 20); árbol.insertar(árbol.raíz, 40); árbol.insertar(árbol.raíz, 70); árbol.insertar(árbol.raíz, 60); árbol.insertar(árbol.raíz, 80); // Clave a encontrar int key = 6; // Buscando en un BST if (tree.search(tree.root, key) == null) System.out.println(key + ' not found'); else System.out.println(clave + ' encontrado'); clave = 60; // Buscando en un BST if (tree.search(tree.root, key) == null) System.out.println(key + ' not found'); else System.out.println(clave + ' encontrado'); } }> |
>
formatear fecha en cadena
>
Python3
# Python3 function to search a given key in a given BST> class> Node:> ># Constructor to create a new node> >def> __init__(>self>, key):> >self>.key>=> key> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> # A utility function to insert> # a new node with the given key in BST> def> insert(node, key):> ># If the tree is empty, return a new node> >if> node>is> None>:> >return> Node(key)> ># Otherwise, recur down the tree> >if> key node.left = insert(node.left, key) elif key>node.key: node.right = insert(node.right, key) # Devuelve el puntero de nodo (sin cambios) return node # Función de utilidad para buscar una clave en una búsqueda BST def (raíz, clave): # Casos base: la raíz es nulo o la clave está presente en la raíz si la raíz es Ninguna o root.key == clave: devuelve raíz # La clave es mayor que la clave de la raíz si raíz.clave devuelve búsqueda (root.right, clave) # La clave es menor que la raíz 's key return search(root.left, key) # Código del controlador if __name__ == '__main__': root = Ninguno root = insert(root, 50) insert(root, 30) insert(root, 20) insert (root, 40) insert(root, 70) insert(root, 60) insert(root, 80) # Clave a encontrar key = 6 # Buscando en un BST si search(root, key) es Ninguno: print(key, 'not found') else: print(key, 'found') key = 60 # Buscando en un BST si la búsqueda(root, key) es Ninguna: print(key, 'not found') else: imprimir(clave, 'encontrado')> |
>
>
C#
// C# function to search a given key in a given BST> using> System;> public> class> Node {> >public> int> key;> >public> Node left, right;> }> public> class> BinaryTree {> >// A utility function to create a new BST node> >public> Node NewNode(>int> item)> >{> >Node temp =>new> Node();> >temp.key = item;> >temp.left = temp.right =>null>;> >return> temp;> >}> >// A utility function to insert> >// a new node with given key in BST> >public> Node Insert(Node node,>int> key)> >{> >// If the tree is empty, return a new node> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> NewNode(key);> >// Otherwise, recur down the tree> >if> (key node.left = Insert(node.left, key); else if (key>nodo.clave) nodo.derecha = Insertar(nodo.derecha, clave); // Devuelve el puntero del nodo (sin cambios) return node; } // Función de utilidad para buscar una clave en una búsqueda de nodo público BST (raíz de nodo, clave int) // Casos base: la raíz es nula o la clave está presente en la raíz if (root == null // Código de controlador public static void Main () { Raíz del nodo = nulo; BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree(); raíz = bt.Insert(raíz, 50); bt.Insert(raíz, 30); , 40); bt.Insert(root, 70); bt.Insert(root, 60); bt.Insert(root, 80); // Clave a encontrar int key = 6; bt.Search(root, key) == null) Console.WriteLine(key + ' not found'); else Console.WriteLine(key + ' found'); if (bt.Search(root, key) == null) Console.WriteLine(key + ' not found'); else Console.WriteLine(key + ' found'); |
>
// Javascript function to search a given key in a given BST>class Node {>>constructor(key) {>>this>.key = key;>>this>.left =>null>;>>this>.right =>null>;>>}>}>// A utility function to insert>// a new node with given key in BST>function>insert(node, key) {>>// If the tree is empty, return a new node>>if>(node ===>null>) {>>return>new>Node(key);>>}>>// Otherwise, recur down the tree>>if>(key node.left = insert(node.left, key); } else if (key>nodo.clave) { nodo.derecha = insertar(nodo.derecha, clave); } // Devuelve el puntero del nodo (sin cambios) return node; } // Función de utilidad para buscar una clave en una función BST search(root, key) { // Casos base: la raíz es nula o la clave está presente en la raíz if (root === null || root.key === key ) {retornar raíz; } // La clave es mayor que la clave de root if (root.key return search(root.right, key); } // La clave es menor que la clave de root return search(root.left, key); } // Código del controlador let root = null; insert (raíz, 50); insert (raíz, 30); insert (raíz, 40); 60); insert(root, 80); // Clave a encontrar let key = 6 // Buscando en un BST if (search(root, key) === null) { console.log(key + ' not encontrado'); } else { console.log(key + ' found'); clave = 60 // Buscando en un BST if (search(root, key) === null) { console.log( clave + ' no encontrado'); } else { console.log(clave + ' encontrado' }>>>Producción6 not found 60 found>Complejidad del tiempo: O(h), donde h es la altura del BST.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(h), donde h es la altura del BST. Esto se debe a que la cantidad máxima de espacio necesaria para almacenar la pila de recursividad sería h .Enlaces relacionados:
- Operación de inserción del árbol de búsqueda binaria
- Operación de eliminación del árbol de búsqueda binaria