En este artículo, analizaremos el algoritmo Quicksort. El procedimiento de trabajo de Quicksort también es sencillo. Este artículo será muy útil e interesante para los estudiantes, ya que podrían enfrentarse a la clasificación rápida como una pregunta en sus exámenes. Por eso es importante discutir el tema.
Ordenar es una forma de organizar elementos de manera sistemática. Quicksort es el algoritmo de clasificación ampliamente utilizado que hace norte iniciar sesión norte comparaciones en caso promedio para ordenar una matriz de n elementos. Es un algoritmo de clasificación más rápido y altamente eficiente. Este algoritmo sigue el enfoque de divide y vencerás. Divide y vencerás es una técnica que consiste en dividir los algoritmos en subproblemas, luego resolverlos y combinar los resultados nuevamente para resolver el problema original.
primera búsqueda en profundidad del algoritmo
Dividir: En Divide, primero elige un elemento pivote. Después de eso, divida o reorganice la matriz en dos submatrizes de modo que cada elemento en la submatriz izquierda sea menor o igual que el elemento pivote y cada elemento en la submatriz derecha sea más grande que el elemento pivote.
Conquistar: De forma recursiva, ordene dos subarreglos con Quicksort.
Combinar: Combina la matriz ya ordenada.
Quicksort elige un elemento como pivote y luego divide la matriz dada alrededor del elemento pivote seleccionado. En la clasificación rápida, una matriz grande se divide en dos matrices en las que una contiene valores menores que el valor especificado (pivote) y otra matriz contiene valores mayores que el pivote.
Después de eso, los subarreglos izquierdo y derecho también se dividen utilizando el mismo enfoque. Continuará hasta que el único elemento permanezca en la submatriz.
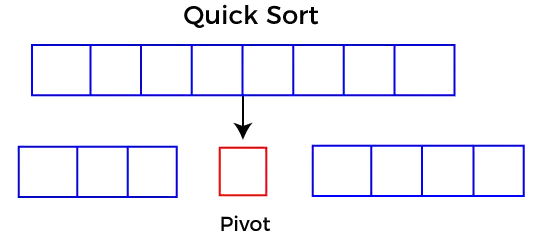
Elegir el pivote
Es necesario elegir un buen pivote para la rápida implementación de Quicksort. Sin embargo, lo habitual es determinar un buen pivote. Algunas de las formas de elegir un pivote son las siguientes:
- El pivote puede ser aleatorio, es decir, seleccione el pivote aleatorio de la matriz dada.
- Pivot puede ser el elemento más a la derecha del elemento más a la izquierda de la matriz dada.
- Seleccione la mediana como elemento pivote.
Algoritmo
Algoritmo:
QUICKSORT (array A, start, end) { 1 if (start <end) 2 3 4 5 6 { p="partition(A," start, end) quicksort (a, - 1) + 1, } < pre> <p> <strong>Partition Algorithm:</strong> </p> <p>The partition algorithm rearranges the sub-arrays in a place.</p> <pre> PARTITION (array A, start, end) { 1 pivot ? A[end] 2 i ? start-1 3 for j ? start to end -1 { 4 do if (A[j] <pivot) 1 5 6 7 8 9 { then i ? + swap a[i] with a[j] }} a[i+1] a[end] return i+1 } < pre> <h2>Working of Quick Sort Algorithm</h2> <p>Now, let's see the working of the Quicksort Algorithm.</p> <p>To understand the working of quick sort, let's take an unsorted array. It will make the concept more clear and understandable.</p> <p>Let the elements of array are -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-2.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>In the given array, we consider the leftmost element as pivot. So, in this case, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 27 and a[pivot] = 24.</p> <p>Since, pivot is at left, so algorithm starts from right and move towards left.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-3.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] <a[right], so algorithm moves forward one position towards left, i.e. -< p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-4.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 19, and a[pivot] = 24.</p> <p>Because, a[pivot] > a[right], so, algorithm will swap a[pivot] with a[right], and pivot moves to right, as -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-5.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 19, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. Since, pivot is at right, so algorithm starts from left and moves to right.</p> <p>As a[pivot] > a[left], so algorithm moves one position to right as -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-6.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 9, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] > a[left], so algorithm moves one position to right as -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-7.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 29, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] <a[left], so, swap a[pivot] and a[left], now pivot is at left, i.e. -< p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-8.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Since, pivot is at left, so algorithm starts from right, and move to left. Now, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 29, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] <a[right], so algorithm moves one position to left, as -< p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-9.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 24, and a[right] = 14. As a[pivot] > a[right], so, swap a[pivot] and a[right], now pivot is at right, i.e. -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-10.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 14, and a[right] = 24. Pivot is at right, so the algorithm starts from left and move to right.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-11.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 24, and a[right] = 24. So, pivot, left and right are pointing the same element. It represents the termination of procedure.</p> <p>Element 24, which is the pivot element is placed at its exact position.</p> <p>Elements that are right side of element 24 are greater than it, and the elements that are left side of element 24 are smaller than it.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-12.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, in a similar manner, quick sort algorithm is separately applied to the left and right sub-arrays. After sorting gets done, the array will be -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-13.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <h2>Quicksort complexity</h2> <p>Now, let's see the time complexity of quicksort in best case, average case, and in worst case. We will also see the space complexity of quicksort.</p> <h3>1. Time Complexity</h3> <table class="table"> <tr> <th>Case</th> <th>Time Complexity</th> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Best Case</strong> </td> <td>O(n*logn)</td> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Average Case</strong> </td> <td>O(n*logn)</td> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Worst Case</strong> </td> <td>O(n<sup>2</sup>)</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <tr><td>Best Case Complexity -</td> In Quicksort, the best-case occurs when the pivot element is the middle element or near to the middle element. The best-case time complexity of quicksort is <strong>O(n*logn)</strong> . </tr><tr><td>Average Case Complexity -</td> It occurs when the array elements are in jumbled order that is not properly ascending and not properly descending. The average case time complexity of quicksort is <strong>O(n*logn)</strong> . </tr><tr><td>Worst Case Complexity -</td> In quick sort, worst case occurs when the pivot element is either greatest or smallest element. Suppose, if the pivot element is always the last element of the array, the worst case would occur when the given array is sorted already in ascending or descending order. The worst-case time complexity of quicksort is <strong>O(n<sup>2</sup>)</strong> . </tr></ul> <p>Though the worst-case complexity of quicksort is more than other sorting algorithms such as <strong>Merge sort</strong> and <strong>Heap sort</strong> , still it is faster in practice. Worst case in quick sort rarely occurs because by changing the choice of pivot, it can be implemented in different ways. Worst case in quicksort can be avoided by choosing the right pivot element.</p> <h3>2. Space Complexity</h3> <table class="table"> <tr> <td> <strong>Space Complexity</strong> </td> <td>O(n*logn)</td> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Stable</strong> </td> <td>NO</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <li>The space complexity of quicksort is O(n*logn).</li> </ul> <h2>Implementation of quicksort</h2> <p>Now, let's see the programs of quicksort in different programming languages.</p> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quicksort in C language.</p> <pre> #include /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ int partition (int a[], int start, int end) { int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element int i = (start - 1); for (int j = start; j <= 27 end - 1; j++) { if current element is smaller than the pivot (a[j] < pivot) i++; increment index of int t="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="t;" } a[i+1]="a[end];" a[end]="t;" return (i + 1); * function to implement quick sort void quick(int a[], start, end) a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, (start p="partition(a," end); partitioning quick(a, 1, print an array printarr(int n) i; for i n; i++) printf('%d ', a[i]); main() 24, 9, 29, 14, 19, }; n="sizeof(a)" sizeof(a[0]); printf('before sorting elements are
'); printarr(a, n); 0, printf('
after 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-14.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quick sort in C++ language.</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ int partition (int a[], int start, int end) { int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element int i = (start - 1); for (int j = start; j <= 26 end - 1; j++) { if current element is smaller than the pivot (a[j] < pivot) i++; increment index of int t="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="t;" } a[i+1]="a[end];" a[end]="t;" return (i + 1); * function to implement quick sort void quick(int a[], start, end) a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, (start p="partition(a," end); partitioning quick(a, 1, print an array printarr(int n) i; for i n; i++) cout< <a[i]<< ' '; main() 23, 8, 28, 13, 18, }; n="sizeof(a)" sizeof(a[0]); cout<<'before sorting elements are
'; printarr(a, n); 0, cout<<'
after 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-15.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quicksort in python.</p> <pre> #function that consider last element as pivot, #place the pivot at its exact position, and place #smaller elements to left of pivot and greater #elements to right of pivot. def partition (a, start, end): i = (start - 1) pivot = a[end] # pivot element for j in range(start, end): # If current element is smaller than or equal to the pivot if (a[j] <= 1 pivot): i="i" + a[i], a[j]="a[j]," a[i] a[i+1], a[end]="a[end]," a[i+1] return (i 1) # function to implement quick sort def quick(a, start, end): a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, end="Ending" index if (start < p="partition(a," end) is partitioning - 1, printarr(a): print the array for in range(len(a)): (a[i], ) a="[68," 13, 49, 58] print('before sorting elements are ') printarr(a) 0, len(a)-1) print('
after pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-16.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quicksort in Java.</p> <pre> public class Quick { /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ int partition (int a[], int start, int end) { int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element int i = (start - 1); for (int j = start; j <= 25 end - 1; j++) { if current element is smaller than the pivot (a[j] < pivot) i++; increment index of int t="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="t;" } a[i+1]="a[end];" a[end]="t;" return (i + 1); * function to implement quick sort void quick(int a[], start, end) a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, (start p="partition(a," end); partitioning quick(a, 1, print an array printarr(int n) i; for i n; i++) system.out.print(a[i] ' '); public static main(string[] args) 13, 18, 27, 2, 19, }; n="a.length;" system.out.println('
before sorting elements are q1="new" quick(); q1.printarr(a, n); q1.quick(a, 0, system.out.println('
after system.out.println(); pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <p>After the execution of above code, the output will be -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-17.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quick sort in php.</p> <pre> <?php /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ function partition (&$a, $start, $end) { $pivot = $a[$end]; // pivot element $i = ($start - 1); for ($j = $start; $j <= $end - 1; $j++) { // If current element is smaller than the pivot if ($a[$j] < $pivot) { $i++; // increment index of smaller element $t = $a[$i]; $a[$i] = $a[$j]; $a[$j] = $t; } } $t = $a[$i+1]; $a[$i+1] = $a[$end]; $a[$end] = $t; return ($i + 1); } /* function to implement quick sort */ function quick(&$a, $start, $end) /* a[] = array to be sorted, start = Starting index, end = Ending index */ { if ($start < $end) { $p = partition($a, $start, $end); //p is partitioning index quick($a, $start, $p - 1); quick($a, $p + 1, $end); } } function printArray($a, $n) { for($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) { print_r($a[$i]); echo ' '; } } $a = array( 89, 47, 2, 17, 8, 19 ); $n = count($a); echo 'Before sorting array elements are - <br>'; printArray($a, $n); quick($a, 0, $n - 1); echo ' <br> After sorting array elements are - <br>'; printArray($a, $n); ?> </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <p>After the execution of above code, the output will be -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-18.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>So, that's all about the article. Hope the article will be helpful and informative to you.</p> <p>This article was not only limited to the algorithm. Along with the algorithm, we have also discussed the quick sort complexity, working, and implementation in different programming languages.</p> <hr></=></pre></=></pre></=></pre></=></pre></a[right],></p></a[left],></p></a[right],></p></pivot)></pre></end)> Producción
Después de la ejecución del código anterior, el resultado será:
ejemplo de formato json

Entonces, eso es todo sobre el artículo. Espero que el artículo le resulte útil e informativo.
Este artículo no se limitó sólo al algoritmo. Junto con el algoritmo, también hemos analizado la complejidad, el funcionamiento y la implementación de la clasificación rápida en diferentes lenguajes de programación.
