Dada la raíz de un Árbol de búsqueda binaria y un numero entero k . La tarea es encontrar el mayor número en el árbol de búsqueda binaria que es menos que o igual a k si no existe tal elemento, imprima -1.
Ejemplos:
Aporte:
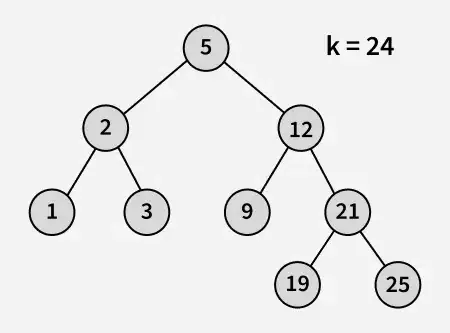
Producción : 21
Explicación : 19 y 25 son los dos números más cercanos a 21 y 19 es el número más grande que tiene un valor menor o igual a 21.
Aporte: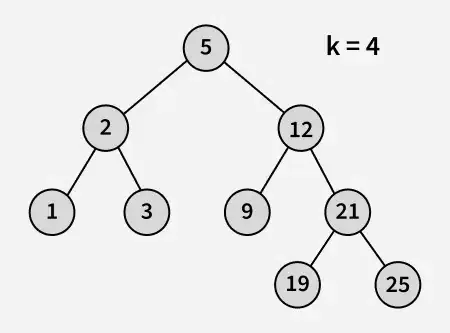
Producción : 3
Explicación : 3 y 5 son los dos números más cercanos a 4 y 3 es el número más grande que tiene un valor menor o igual a 4.
Tabla de contenido
- [Enfoque ingenuo] Uso de la recursividad: tiempo O(h) y espacio O(h)
- [Enfoque esperado] Uso de iteración: tiempo O(h) y espacio O(1)
[Enfoque ingenuo] Uso de la recursividad: tiempo O(h) y espacio O(h)
C++La idea es empezar por el raíz y comparar su valor con k. Si el valor del nodo es mayor que k, muévase al subárbol izquierdo. De lo contrario, encuentre el valor del número más grande menor que k en el subárbol derecho . Si el subárbol derecho devuelve -1 (lo que significa que no existe dicho valor), devuelve el valor del nodo actual. De lo contrario, devolverá el valor devuelto por el subárbol derecho (ya que será mayor que el valor del nodo actual pero menor que k).
// C++ code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion #include
// Java code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int findMaxFork(Node root int k) { // Base cases if (root == null) return -1; if (root.data == k) return k; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if (root.data < k) { int x = findMaxFork(root.right k); if (x == -1) return root.data; else return x; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork(root.left k); } public static void main(String[] args) { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); System.out.println(findMaxFork(root k)); } }
# Python code to find the largest value # smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node: def __init__(self val): self.data = val self.left = None self.right = None # function to find max value less than k def findMaxFork(root k): # Base cases if root is None: return -1 if root.data == k: return k # If root's value is smaller # try in right subtree elif root.data < k: x = findMaxFork(root.right k) if x == -1: return root.data else: return x # If root's data is greater # return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork(root.left k) if __name__ == '__main__': k = 24 # creating following BST # # 5 # / # 2 12 # / / # 1 3 9 21 # / # 19 25 root = Node(5) root.left = Node(2) root.left.left = Node(1) root.left.right = Node(3) root.right = Node(12) root.right.left = Node(9) root.right.right = Node(21) root.right.right.left = Node(19) root.right.right.right = Node(25) print(findMaxFork(root k))
// C# code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int FindMaxFork(Node root int k) { // Base cases if (root == null) return -1; if (root.data == k) return k; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if (root.data < k) { int x = FindMaxFork(root.right k); if (x == -1) return root.data; else return x; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return FindMaxFork(root.left k); } static void Main() { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); Console.WriteLine(FindMaxFork(root k)); } }
// JavaScript code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // function to find max value less than k function findMaxFork(root k) { // Base cases if (root === null) return -1; if (root.data === k) return k; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if (root.data < k) { let x = findMaxFork(root.right k); if (x === -1) return root.data; else return x; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork(root.left k); } let k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 let root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); console.log(findMaxFork(root k));
Producción
21
[Enfoque esperado] Uso de iteración: tiempo O(h) y espacio O(1)
C++La idea es empezar por el raíz y comparar su valor con k . Si el valor del nodo es <= k actualice el valor del resultado al valor de la raíz y muévase al bien subárbol, de lo contrario se mueve al izquierda subárbol. Por iterativamente Al aplicar esta operación en todos los nodos, podemos minimizar el espacio necesario para el recursividad pila.
// C++ code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion #include
// Java code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int findMaxFork(Node root int k) { int result = -1; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while (root != null) { // If root is smaller go to right side if (root.data <= k) { result = root.data; root = root.right; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root.left; } } return result; } public static void main(String[] args) { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); System.out.println(findMaxFork(root k)); } }
# Python code to find the largest value # smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node: def __init__(self val): self.data = val self.left = None self.right = None # function to find max value less than k def findMaxFork(root k): result = -1 # Start from root and keep looking for larger while root is not None: # If root is smaller go to right side if root.data <= k: result = root.data root = root.right # If root is greater go to left side else: root = root.left return result if __name__ == '__main__': k = 24 # creating following BST # # 5 # / # 2 12 # / / # 1 3 9 21 # / # 19 25 root = Node(5) root.left = Node(2) root.left.left = Node(1) root.left.right = Node(3) root.right = Node(12) root.right.left = Node(9) root.right.right = Node(21) root.right.right.left = Node(19) root.right.right.right = Node(25) print(findMaxFork(root k))
// C# code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int FindMaxFork(Node root int k) { int result = -1; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while (root != null) { // If root is smaller go to right side if (root.data <= k) { result = root.data; root = root.right; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root.left; } } return result; } static void Main() { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); Console.WriteLine(FindMaxFork(root k)); } }
// JavaScript code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // function to find max value less than k function findMaxFork(root k) { let result = -1; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while (root !== null) { // If root is smaller go to right side if (root.data <= k) { result = root.data; root = root.right; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root.left; } } return result; } let k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 let root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); console.log(findMaxFork(root k));
Producción
21Crear cuestionario


