Introducción:
Los acortadores de URL son un ejemplo de hash, ya que asignan URL de gran tamaño a tamaños pequeños.
Algunos ejemplos de funciones hash:
- % clave número de depósitos
- Valor ASCII del carácter * PrimeNumberX. Donde x = 1, 2, 3….n
- Puede crear su propia función hash, pero debería ser una buena función hash que proporcione menos colisiones.
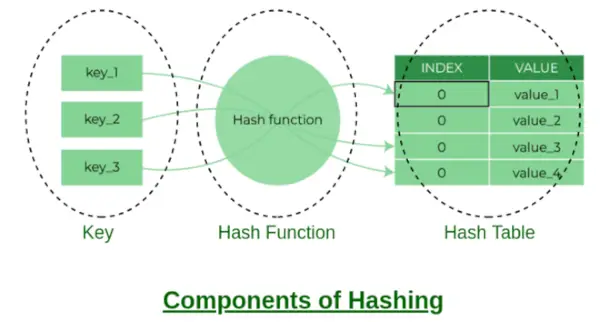
Componentes del hash
convertir caracteres a int java
Índice de cubeta:
El valor devuelto por la función Hash es el índice del depósito para una clave en un método de encadenamiento separado. Cada índice de la matriz se denomina depósito, ya que es un depósito de una lista vinculada.
Refrito:
El refrito es un concepto que reduce la colisión cuando se aumentan los elementos en la tabla hash actual. Creará una nueva matriz de tamaño duplicado y copiará en ella los elementos de la matriz anterior y es como el funcionamiento interno del vector en C++. Obviamente, la función Hash debe ser dinámica ya que debería reflejar algunos cambios cuando se aumenta la capacidad. La función hash incluye la capacidad de la tabla hash, por lo tanto, al copiar valores clave de la función hash de matriz anterior, se obtienen diferentes índices de depósito, ya que depende de la capacidad (depósitos) de la tabla hash. Generalmente, cuando el valor del factor de carga es superior a 0,5, se realizan repetidos.
- Duplica el tamaño de la matriz.
- Copie los elementos de la matriz anterior a la nueva matriz. Usamos la función hash mientras copiamos cada nodo a una nueva matriz nuevamente, por lo tanto, reducirá la colisión.
- Elimine la matriz anterior de la memoria y apunte el puntero interno de la matriz de su mapa hash a esta nueva matriz.
- Generalmente, Factor de carga = número de elementos en Hash Map / número total de depósitos (capacidad).
Colisión:
La colisión es la situación en la que el índice del depósito no está vacío. Significa que hay un encabezado de lista vinculado en ese índice de depósito. Tenemos dos o más valores que se asignan al mismo índice de depósito.
Funciones principales en nuestro programa
- Inserción
- Buscar
- Función hash
- Borrar
- Refrito
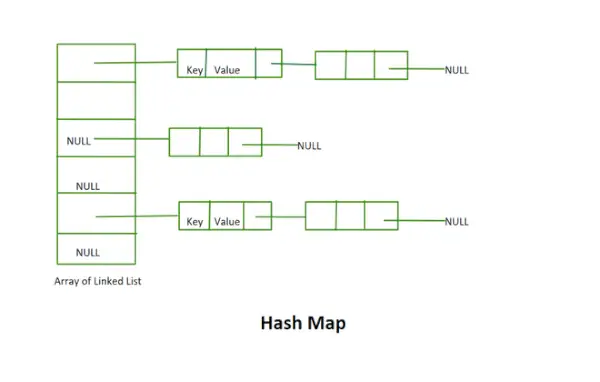
Mapa hash
Implementación sin repetición:
C
#include> #include> #include> // Linked List node> struct> node {> >// key is string> >char>* key;> >// value is also string> >char>* value;> >struct> node* next;> };> // like constructor> void> setNode(>struct> node* node,>char>* key,>char>* value)> {> >node->clave = clave;> >node->valor = valor;> >node->siguiente = NULL;> >return>;> };> struct> hashMap {> >// Current number of elements in hashMap> >// and capacity of hashMap> >int> numOfElements, capacity;> >// hold base address array of linked list> >struct> node** arr;> };> // like constructor> void> initializeHashMap(>struct> hashMap* mp)> {> >// Default capacity in this case> >mp->capacidad = 100;> >mp->númeroDeElementos = 0;> >// array of size = 1> >mp->arr = (>struct> node**)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> node*)> >* mp->capacidad);> >return>;> }> int> hashFunction(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key)> {> >int> bucketIndex;> >int> sum = 0, factor = 31;> >for> (>int> i = 0; i <>strlen>(key); i++) {> >// sum = sum + (ascii value of> >// char * (primeNumber ^ x))...> >// where x = 1, 2, 3....n> >sum = ((sum % mp->capacidad)> >+ (((>int>)key[i]) * factor) % mp->capacidad)> >% mp->capacidad;> >// factor = factor * prime> >// number....(prime> >// number) ^ x> >factor = ((factor % __INT16_MAX__)> >* (31 % __INT16_MAX__))> >% __INT16_MAX__;> >}> >bucketIndex = sum;> >return> bucketIndex;> }> void> insert(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key,>char>* value)> {> >// Getting bucket index for the given> >// key - value pair> >int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> >struct> node* newNode = (>struct> node*)>malloc>(> >// Creating a new node> >sizeof>(>struct> node));> >// Setting value of node> >setNode(newNode, key, value);> >// Bucket index is empty....no collision> >if> (mp->arr[bucketIndex] == NULL) {> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = nuevoNodo;> >}> >// Collision> >else> {> >// Adding newNode at the head of> >// linked list which is present> >// at bucket index....insertion at> >// head in linked list> >newNode->siguiente = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = nuevoNodo;> >}> >return>;> }> void> delete> (>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key)> {> >// Getting bucket index for the> >// given key> >int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> >struct> node* prevNode = NULL;> >// Points to the head of> >// linked list present at> >// bucket index> >struct> node* currNode = mp->arr[índicedebucket];> >while> (currNode != NULL) {> >// Key is matched at delete this> >// node from linked list> >if> (>strcmp>(key, currNode->clave) == 0) {> >// Head node> >// deletion> >if> (currNode == mp->arr[índicedebucket]) {> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = currNode->siguiente;> >}> >// Last node or middle node> >else> {> >prevNode->siguiente = currNode->siguiente;> >}> >free>(currNode);> >break>;> >}> >prevNode = currNode;> >currNode = currNode->siguiente;> >}> >return>;> }> char>* search(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key)> {> >// Getting the bucket index> >// for the given key> >int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> >// Head of the linked list> >// present at bucket index> >struct> node* bucketHead = mp->arr[índicedebucket];> >while> (bucketHead != NULL) {> >// Key is found in the hashMap> >if> (bucketHead->clave == clave) {> >return> bucketHead->valor;> >}> >bucketHead = bucketHead->siguiente;> >}> >// If no key found in the hashMap> >// equal to the given key> >char>* errorMssg = (>char>*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>char>) * 25);> >errorMssg =>'Oops! No data found.
'>;> >return> errorMssg;> }> // Drivers code> int> main()> {> >// Initialize the value of mp> >struct> hashMap* mp> >= (>struct> hashMap*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> hashMap));> >initializeHashMap(mp);> >insert(mp,>'Yogaholic'>,>'Anjali'>);> >insert(mp,>'pluto14'>,>'Vartika'>);> >insert(mp,>'elite_Programmer'>,>'Manish'>);> >insert(mp,>'GFG'>,>'techcodeview.com'>);> >insert(mp,>'decentBoy'>,>'Mayank'>);> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'elite_Programmer'>));> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'Yogaholic'>));> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'pluto14'>));> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'decentBoy'>));> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'GFG'>));> >// Key is not inserted> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'randomKey'>));> >printf>(>'
After deletion :
'>);> >// Deletion of key> >delete> (mp,>'decentBoy'>);> >printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'decentBoy'>));> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
C++
#include> #include> // Linked List node> struct> node {> >// key is string> >char>* key;> >// value is also string> >char>* value;> >struct> node* next;> };> // like constructor> void> setNode(>struct> node* node,>char>* key,>char>* value) {> >node->clave = clave;> >node->valor = valor;> >node->siguiente = NULL;> >return>;> }> struct> hashMap {> >// Current number of elements in hashMap> >// and capacity of hashMap> >int> numOfElements, capacity;> >// hold base address array of linked list> >struct> node** arr;> };> // like constructor> void> initializeHashMap(>struct> hashMap* mp) {> >// Default capacity in this case> >mp->capacidad = 100;> >mp->númeroDeElementos = 0;> >// array of size = 1> >mp->arr = (>struct> node**)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> node*) * mp->capacidad);> >return>;> }> int> hashFunction(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key) {> >int> bucketIndex;> >int> sum = 0, factor = 31;> >for> (>int> i = 0; i <>strlen>(key); i++) {> >// sum = sum + (ascii value of> >// char * (primeNumber ^ x))...> >// where x = 1, 2, 3....n> >sum = ((sum % mp->capacidad) + (((>int>)key[i]) * factor) % mp->capacidad) % mp->capacidad;> >// factor = factor * prime> >// number....(prime> >// number) ^ x> >factor = ((factor % __INT16_MAX__) * (31 % __INT16_MAX__)) % __INT16_MAX__;> >}> >bucketIndex = sum;> >return> bucketIndex;> }> void> insert(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key,>char>* value) {> >// Getting bucket index for the given> >// key - value pair> >int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> >struct> node* newNode = (>struct> node*)>malloc>(> >// Creating a new node> >sizeof>(>struct> node));> >// Setting value of node> >setNode(newNode, key, value);> >// Bucket index is empty....no collision> >if> (mp->arr[bucketIndex] == NULL) {> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = nuevoNodo;> >}> >// Collision> >else> {> >// Adding newNode at the head of> >// linked list which is present> >// at bucket index....insertion at> >// head in linked list> >newNode->siguiente = mp->arr[bucketIndex];> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = nuevoNodo;> >}> >return>;> }> void> deleteKey(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key) {> >// Getting bucket index for the> >// given key> >int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> >struct> node* prevNode = NULL;> >// Points to the head of> >// linked list present at> >// bucket index> >struct> node* currNode = mp->arr[índicedebucket];> >while> (currNode != NULL) {> >// Key is matched at delete this> >// node from linked list> >if> (>strcmp>(key, currNode->clave) == 0) {> >// Head node> >// deletion> >if> (currNode == mp->arr[índicedebucket]) {> >mp->arr[bucketIndex] = currNode->siguiente;> >}> >// Last node or middle node> >else> {> >prevNode->siguiente = currNode->siguiente;> }> free>(currNode);> break>;> }> prevNode = currNode;> >currNode = currNode->siguiente;> >}> return>;> }> char>* search(>struct> hashMap* mp,>char>* key) {> // Getting the bucket index for the given key> int> bucketIndex = hashFunction(mp, key);> // Head of the linked list present at bucket index> struct> node* bucketHead = mp->arr[índicedebucket];> while> (bucketHead != NULL) {> > >// Key is found in the hashMap> >if> (>strcmp>(bucketHead->clave, clave) == 0) {> >return> bucketHead->valor;> >}> > >bucketHead = bucketHead->siguiente;> }> // If no key found in the hashMap equal to the given key> char>* errorMssg = (>char>*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>char>) * 25);> strcpy>(errorMssg,>'Oops! No data found.
'>);> return> errorMssg;> }> // Drivers code> int> main()> {> // Initialize the value of mp> struct> hashMap* mp = (>struct> hashMap*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> hashMap));> initializeHashMap(mp);> insert(mp,>'Yogaholic'>,>'Anjali'>);> insert(mp,>'pluto14'>,>'Vartika'>);> insert(mp,>'elite_Programmer'>,>'Manish'>);> insert(mp,>'GFG'>,>'techcodeview.com'>);> insert(mp,>'decentBoy'>,>'Mayank'>);> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'elite_Programmer'>));> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'Yogaholic'>));> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'pluto14'>));> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'decentBoy'>));> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'GFG'>));> // Key is not inserted> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'randomKey'>));> printf>(>'
After deletion :
'>);> // Deletion of key> deleteKey(mp,>'decentBoy'>);> // Searching the deleted key> printf>(>'%s
'>, search(mp,>'decentBoy'>));> return> 0;> }> |
>
cadena en matriz c
>Producción
Manish Anjali Vartika Mayank techcodeview.com Oops! No data found. After deletion : Oops! No data found.>
Explicación:
- inserción: inserta el par clave-valor al principio de una lista vinculada que está presente en el índice del depósito determinado. hashFunction: proporciona el índice del depósito para la clave dada. Nuestro función hash = valor ASCII del carácter * número primoX . El número primo en nuestro caso es 31 y el valor de x aumenta de 1 a n para caracteres consecutivos en una clave. eliminación: elimina el par clave-valor de la tabla hash para la clave dada. Elimina el nodo de la lista vinculada que contiene el par clave-valor. Buscar: busca el valor de la clave dada.
- Esta implementación no utiliza el concepto de repetición. Es una matriz de listas enlazadas de tamaño fijo.
- Tanto la clave como el valor son cadenas en el ejemplo dado.
Complejidad temporal y complejidad espacial:
La complejidad temporal de las operaciones de inserción y eliminación de tablas hash es O(1) en promedio. Hay algún cálculo matemático que lo demuestra.
- Complejidad temporal de la inserción: En el caso promedio es constante. En el peor de los casos, es lineal. Complejidad temporal de la búsqueda: En el caso promedio es constante. En el peor de los casos, es lineal. Complejidad temporal de la eliminación: en casos promedio es constante. En el peor de los casos, es lineal. Complejidad espacial: O (n) ya que tiene n número de elementos.
Artículos relacionados:
- Técnica de manejo de colisiones de encadenamiento separado en Hashing.
