En Java, Heap es un tipo especial de estructura de datos donde el nodo raíz o el nodo padre se compara con sus hijos izquierdo y derecho y se organiza según el orden. Supongamos que x es un nodo raíz e y es el nodo secundario, propiedad clave(x)<= key(y)< strong>generará un montón mínimo, y esa relación se conoce como 'Propiedad del montón' .
Según el orden de los nodos padre e hijo, el montón se puede clasificar en dos formas, es decir, montón mínimo y montón máximo. Comprendamos ambos uno por uno e implementemos el código en Java.
montón mínimo
El montón mínimo es un tipo especial de estructura de datos de montón que es un árbol binario completo en sí mismo. El montón mínimo tiene las siguientes propiedades:
- El valor del nodo raíz siempre es menor en comparación con los otros nodos del montón.
- Cada nodo interno tiene un valor clave que siempre es menor o igual que sus hijos.
Podemos realizar las siguientes tres operaciones en el montón mínimo:
insertarNodo()
Podemos realizar la inserción en el montón Min agregando una nueva clave al final del árbol. Si el valor de la clave insertada es menor que su nodo principal, tenemos que recorrer la clave hacia arriba para cumplir con la propiedad del montón. El proceso de inserción lleva O(log n) tiempo.
extraerMin()
Es una de las operaciones más importantes que realizamos para eliminar el nodo de valor mínimo, es decir, el nodo raíz del montón. Después de eliminar el nodo raíz, debemos asegurarnos de que se mantenga la propiedad del montón. La operación extractMin() tarda O(Logn) en eliminar el elemento mínimo del montón.
obtenerMín()
El obtenerMín() La operación se utiliza para obtener el nodo raíz del montón, es decir, el elemento mínimo en tiempo O(1).
Ejemplo:
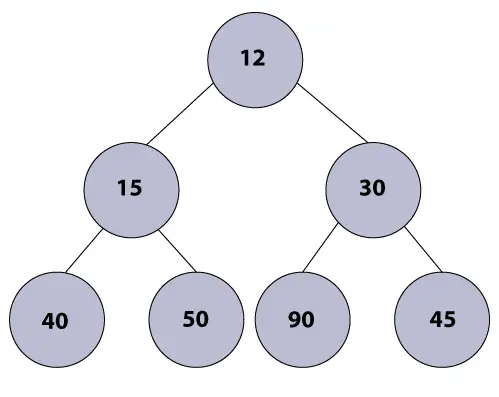
Algoritmo de montón mínimo
proceduredesign_min_heap Array arr: of size n => array of elements // call min_heapify procedure for each element of the array to form min heap repeat for (k = n/2 ; k >= 1 ; k--) call procedure min_heapify (arr, k); proceduremin_heapify (vararr[ ] , var k, varn) { varleft_child = 2*k; varright_child = 2*k+1; var smallest; if(left_child<= n and arr[left_child ] <arr[ k ) smallest="left_child;" else if(right_child<="n" arr[right_child <arr[smallest] if(smallest !="k)" { swaparr[ arr[ ]); callmin_heapify (arr, smallest, n); } < pre> <p> <strong>MinHeapJavaImplementation.java</strong> </p> <pre> // import required classes and packages packagejavaTpoint.javacodes; importjava.util.Scanner; // create class MinHeap to construct Min heap in Java classMinHeap { // declare array and variables privateint[] heapData; privateintsizeOfHeap; privateintheapMaxSize; private static final int FRONT = 1; //use constructor to initialize heapData array publicMinHeap(intheapMaxSize) { this.heapMaxSize = heapMaxSize; this.sizeOfHeap = 0; heapData = new int[this.heapMaxSize + 1]; heapData[0] = Integer.MIN_VALUE; } // create getParentPos() method that returns parent position for the node privateintgetParentPosition(int position) { return position / 2; } // create getLeftChildPosition() method that returns the position of left child privateintgetLeftChildPosition(int position) { return (2 * position); } // create getRightChildPosition() method that returns the position of right child privateintgetRightChildPosition(int position) { return (2 * position) + 1; } // checks whether the given node is leaf or not privatebooleancheckLeaf(int position) { if (position >= (sizeOfHeap / 2) && position heapData[getLeftChildPosition(position)] || heapData[position] >heapData[getRightChildPosition(position)]) { // swap with left child and then heapify the left child if (heapData[getLeftChildPosition(position)] = heapMaxSize) { return; } heapData[++sizeOfHeap] = data; int current = sizeOfHeap; while (heapData[current] <heapdata[getparentposition(current)]) { swap(current, getparentposition(current)); current="getParentPosition(current);" } crreatedisplayheap() method to print the data of heap public void displayheap() system.out.println('parent node' + ' ' 'left child 'right node'); for (int k="1;" position--) minheapify(position); create removeroot() removing minimum element from publicintremoveroot() intpopelement="heapData[FRONT];" heapdata[front]="heapData[sizeOfHeap--];" minheapify(front); returnpopelement; minheapjavaimplementation class in java classminheapjavaimplementation{ main() start static main(string[] arg) declare variable intheapsize; scanner object sc="new" scanner(system.in); system.out.println('enter size min heap'); heapsize="sc.nextInt();" minheapheapobj="new" minheap(heapsize); for(inti="1;" i<="heapSize;" i++) system.out.print('enter '+i+' element: '); int heapobj.insertnode(data); close obj sc.close(); construct a given heapobj.designminheap(); display system.out.println('the is heapobj.displayheap(); root node system.out.println('after element(root node) '+heapobj.removeroot()+', is:'); < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/97/heap-implementation-java-2.webp" alt="Heap implementation in Java"> <h2>Max heap</h2> <p>Max heap is another special type of heap data structure that is also a complete binary tree in itself in Java. Max heap has the following properties:</p> <ol class="points"> <li>Root node value is always greater in comparison to the other nodes of the heap.</li> <li>Each internal node has a key value that is always greater or equal to its children.</li> </ol> <p>We can perform the following three operations in Max heap:</p> <h3>insertNode()</h3> <p>We can perform insertion in the Max heap by adding a new key at the end of the tree. If the value of the inserted key is greater than its parent node, we have to traverse the key upwards for fulfilling the heap property. The insertion process takes O(log n) time.</p> <h3>extractMax()</h3> <p>It is one of the most important operations which we perform to remove the maximum value node, i.e., the root node of the heap. After removing the root node, we have to make sure that heap property should be maintained. The extractMax() operation takes O(Log n) time to remove the maximum element from the heap.</p> <h3>getMax()</h3> <p>The <strong>getMax()</strong> operation is used to get the root node of the heap, i.e., maximum element in O(1) time.</p> <p> <strong>Example:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/97/heap-implementation-java-3.webp" alt="Heap implementation in Java"> <p> <strong>Min heap Algorithm</strong> </p> <pre> proceduredesign_max_heap Array arr: of size n => array of elements // call min_heapify procedure for each element of the array to form max heap repeat for (k = n/2 ; k >= 1 ; k--) call procedure max_heapify (arr, k); proceduremin_heapify (vararr[ ] , var k, varn) { varleft_child = 2*k + 1; varright_child = 2*k+ 2; if(left_childarr[ largest ] ) largest = left_child; else largest = k; if(right_childarr[largest] ) largest = right_child; if(largest != k) { swaparr[ k ] and arr[ largest ]); callmax_heapify (arr, largest, n); } } </pre> <p> <strong>MaxHeapJavaImplementation.java</strong> </p> <pre> //import required classes and packages packagejavaTpoint.javacodes; importjava.util.Scanner; //create class MinHeap to construct Min heap in Java classMaxHeap { // declare array and variables privateint[] heapData; privateintsizeOfHeap; privateintheapMaxSize; private static final int FRONT = 1; //use constructor to initialize heapData array publicMaxHeap(intheapMaxSize) { this.heapMaxSize = heapMaxSize; this.sizeOfHeap = 0; heapData = new int[this.heapMaxSize]; } // create getParentPos() method that returns parent position for the node privateintgetParentPosition(int position) { return (position - 1) / 2; } // create getLeftChildPosition() method that returns the position of left child privateintgetLeftChildPosition(int position) { return (2 * position); } // create getRightChildPosition() method that returns the position of right child privateintgetRightChildPosition(int position) { return (2 * position) + 1; } // checks whether the given node is leaf or not privatebooleancheckLeaf(int position) { if (position > (sizeOfHeap / 2) && position <= sizeofheap) { return true; } false; create swapnodes() method that perform swapping of the given nodes heap firstnode and secondnode are positions private void swap(intfirstnode, intsecondnode) int temp; temp="heapData[firstNode];" heapdata[firstnode]="heapData[secondNode];" heapdata[secondnode]="temp;" maxheapify() to heapify node for maintaining property maxheapify(int position) check whether is non-leaf greater than its right left child if (!checkleaf(position)) (heapdata[position] <heapdata[getleftchildposition(position)] || heapdata[position] heapdata[getrightchildposition(position)]) swap(position, getleftchildposition(position)); maxheapify(getleftchildposition(position)); swap with else getrightchildposition(position)); maxheapify(getrightchildposition(position)); insertnode() insert element in public insertnode(int data) heapdata[sizeofheap]="data;" current="sizeOfHeap;" while (heapdata[current]>heapData[getParentPosition(current)]) { swap(current, getParentPosition(current)); current = getParentPosition(current); } sizeOfHeap++; } // create displayHeap() method to print the data of the heap public void displayHeap() { System.out.println('PARENT NODE' + ' ' + 'LEFT CHILD NODE' + ' ' + 'RIGHT CHILD NODE'); for (int k = 0; k <sizeofheap 2; k++) { system.out.print(' ' + heapdata[k] ' ' heapdata[2 * k 1] 2]); system.out.println(); } create designmaxheap() method to construct min heap public void for (int position="0;" < (sizeofheap 2); position++) maxheapify(position); removeroot() removing maximum element from the publicintremoveroot() intpopelement="heapData[FRONT];" heapdata[front]="heapData[sizeOfHeap--];" maxheapify(front); returnpopelement; minheapjavaimplementation class in java classmaxheapjavaimplementation{ main() start static main(string[] arg) declare variable intheapsize; scanner object sc="new" scanner(system.in); system.out.println('enter size of max heap'); heapsize="sc.nextInt();" maxheapheapobj="new" maxheap(50); for(inti="1;" i<="heapSize;" i++) system.out.print('enter '+i+' element: '); int data="sc.nextInt();" heapobj.insertnode(data); close obj sc.close(); a given heapobj.designmaxheap(); display system.out.println('the is heapobj.displayheap(); root node system.out.println('after element(root node) '+heapobj.removeroot()+', is:'); pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/97/heap-implementation-java-4.webp" alt="Heap implementation in Java"> <hr></sizeofheap></=></pre></heapdata[getparentposition(current)])></pre></=> MaxHeapJavaImplementation.java
//import required classes and packages packagejavaTpoint.javacodes; importjava.util.Scanner; //create class MinHeap to construct Min heap in Java classMaxHeap { // declare array and variables privateint[] heapData; privateintsizeOfHeap; privateintheapMaxSize; private static final int FRONT = 1; //use constructor to initialize heapData array publicMaxHeap(intheapMaxSize) { this.heapMaxSize = heapMaxSize; this.sizeOfHeap = 0; heapData = new int[this.heapMaxSize]; } // create getParentPos() method that returns parent position for the node privateintgetParentPosition(int position) { return (position - 1) / 2; } // create getLeftChildPosition() method that returns the position of left child privateintgetLeftChildPosition(int position) { return (2 * position); } // create getRightChildPosition() method that returns the position of right child privateintgetRightChildPosition(int position) { return (2 * position) + 1; } // checks whether the given node is leaf or not privatebooleancheckLeaf(int position) { if (position > (sizeOfHeap / 2) && position <= sizeofheap) { return true; } false; create swapnodes() method that perform swapping of the given nodes heap firstnode and secondnode are positions private void swap(intfirstnode, intsecondnode) int temp; temp="heapData[firstNode];" heapdata[firstnode]="heapData[secondNode];" heapdata[secondnode]="temp;" maxheapify() to heapify node for maintaining property maxheapify(int position) check whether is non-leaf greater than its right left child if (!checkleaf(position)) (heapdata[position] <heapdata[getleftchildposition(position)] || heapdata[position] heapdata[getrightchildposition(position)]) swap(position, getleftchildposition(position)); maxheapify(getleftchildposition(position)); swap with else getrightchildposition(position)); maxheapify(getrightchildposition(position)); insertnode() insert element in public insertnode(int data) heapdata[sizeofheap]="data;" current="sizeOfHeap;" while (heapdata[current]>heapData[getParentPosition(current)]) { swap(current, getParentPosition(current)); current = getParentPosition(current); } sizeOfHeap++; } // create displayHeap() method to print the data of the heap public void displayHeap() { System.out.println('PARENT NODE' + ' ' + 'LEFT CHILD NODE' + ' ' + 'RIGHT CHILD NODE'); for (int k = 0; k <sizeofheap 2; k++) { system.out.print(\' \' + heapdata[k] \' \' heapdata[2 * k 1] 2]); system.out.println(); } create designmaxheap() method to construct min heap public void for (int position="0;" < (sizeofheap 2); position++) maxheapify(position); removeroot() removing maximum element from the publicintremoveroot() intpopelement="heapData[FRONT];" heapdata[front]="heapData[sizeOfHeap--];" maxheapify(front); returnpopelement; minheapjavaimplementation class in java classmaxheapjavaimplementation{ main() start static main(string[] arg) declare variable intheapsize; scanner object sc="new" scanner(system.in); system.out.println(\'enter size of max heap\'); heapsize="sc.nextInt();" maxheapheapobj="new" maxheap(50); for(inti="1;" i<="heapSize;" i++) system.out.print(\'enter \'+i+\' element: \'); int data="sc.nextInt();" heapobj.insertnode(data); close obj sc.close(); a given heapobj.designmaxheap(); display system.out.println(\'the is heapobj.displayheap(); root node system.out.println(\'after element(root node) \'+heapobj.removeroot()+\', is:\'); pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/97/heap-implementation-java-4.webp" alt="Heap implementation in Java"> <hr></sizeofheap></=>