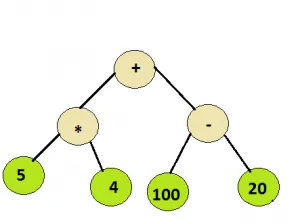
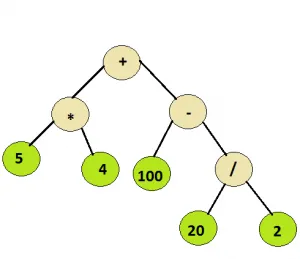
Dado un simple árbol de expresión que consta de operadores binarios básicos, es decir, + - * y / y algunos números enteros evalúan el árbol de expresión.
Ejemplos:
Práctica recomendada Árbol de expresión ¡Pruébalo!Aporte: Nodo raíz del árbol siguiente
Producción: 100
Aporte: Nodo raíz del árbol siguiente
¿Qué es el envío de directorio?
Producción: 110
Acercarse: El enfoque para resolver este problema se basa en la siguiente observación:
Como todos los operadores del árbol son binarios, cada nodo tendrá 0 o 2 hijos. Como se puede inferir de los ejemplos anteriores, todos los valores enteros aparecerían en los nodos hoja, mientras que los nodos interiores representan los operadores.
Por lo tanto podemos hacer recorrido en orden del árbol binario y evaluar la expresión a medida que avanzamos.
Para evaluar el árbol de sintaxis se puede seguir un enfoque recursivo.
Algoritmo:
- Sea t el árbol de sintaxis
- Si t no es nulo entonces
- Si t.info es operando entonces
- Volver t.info
- Demás
- A = resolver(t.izquierda)
- B = resolver(t.derecha)
- devolver A operador B donde operador es la información contenida en t
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++// C++ program to evaluate an expression tree #include
// Java program to evaluate expression tree import java.lang.*; class GFG{ Node root; // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree public static class Node { String data; Node left right; Node(String d) { data = d; left = null; right = null; } } private static int toInt(String s) { int num = 0; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate // the number normally if (s.charAt(0) != '-') for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) num = num * 10 + ((int)s.charAt(i) - 48); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for(int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++) num = num * 10 + ((int)(s.charAt(i)) - 48); num = num * -1; } return num; } // This function receives a node of the syntax // tree and recursively evaluate it public static int evalTree(Node root) { // Empty tree if (root == null) return 0; // Leaf node i.e an integer if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return toInt(root.data); // Evaluate left subtree int leftEval = evalTree(root.left); // Evaluate right subtree int rightEval = evalTree(root.right); // Check which operator to apply if (root.data.equals('+')) return leftEval + rightEval; if (root.data.equals('-')) return leftEval - rightEval; if (root.data.equals('*')) return leftEval * rightEval; return leftEval / rightEval; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a sample tree Node root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('-4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('20'); System.out.println(evalTree(root)); root = null; // Creating a sample tree root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('/'); root.right.right.left = new Node('20'); root.right.right.right = new Node('2'); System.out.println(evalTree(root)); } } // This code is contributed by Ankit Gupta
# Python program to evaluate expression tree # Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree class node: def __init__(self value): self.left = None self.data = value self.right = None # This function receives a node of the syntax tree # and recursively evaluate it def evaluateExpressionTree(root): # empty tree if root is None: return 0 # leaf node if root.left is None and root.right is None: return int(root.data) # evaluate left tree left_sum = evaluateExpressionTree(root.left) # evaluate right tree right_sum = evaluateExpressionTree(root.right) # check which operation to apply if root.data == '+': return left_sum + right_sum elif root.data == '-': return left_sum - right_sum elif root.data == '*': return left_sum * right_sum else: return left_sum // right_sum # Driver function to test above problem if __name__ == '__main__': # creating a sample tree root = node('+') root.left = node('*') root.left.left = node('5') root.left.right = node('-4') root.right = node('-') root.right.left = node('100') root.right.right = node('20') print (evaluateExpressionTree(root)) root = None # creating a sample tree root = node('+') root.left = node('*') root.left.left = node('5') root.left.right = node('4') root.right = node('-') root.right.left = node('100') root.right.right = node('/') root.right.right.left = node('20') root.right.right.right = node('2') print (evaluateExpressionTree(root)) # This code is contributed by Harshit Sidhwa
// C# program to evaluate expression tree using System; public class GFG { // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree public class Node { public String data; public Node left right; public Node(String d) { data = d; left = null; right = null; } } private static int toInt(String s) { int num = 0; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate // the number normally if (s[0] != '-') for (int i = 0; i < s.Length; i++) num = num * 10 + ((int) s[i] - 48); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for (int i = 1; i < s.Length; i++) num = num * 10 + ((int) (s[i]) - 48); num = num * -1; } return num; } // This function receives a node of the syntax // tree and recursively evaluate it public static int evalTree(Node root) { // Empty tree if (root == null) return 0; // Leaf node i.e an integer if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return toInt(root.data); // Evaluate left subtree int leftEval = evalTree(root.left); // Evaluate right subtree int rightEval = evalTree(root.right); // Check which operator to apply if (root.data.Equals('+')) return leftEval + rightEval; if (root.data.Equals('-')) return leftEval - rightEval; if (root.data.Equals('*')) return leftEval * rightEval; return leftEval / rightEval; } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { // Creating a sample tree Node root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('-4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('20'); Console.WriteLine(evalTree(root)); root = null; // Creating a sample tree root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('/'); root.right.right.left = new Node('20'); root.right.right.right = new Node('2'); Console.WriteLine(evalTree(root)); } } // This code is contributed by umadevi9616
<script> // javascript program to evaluate expression tree var root; // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } function toInt( s) { var num = 0; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate // the number normally if (s.charAt(0) != '-') for (i = 0; i < s.length; i++) num = num * 10 + ( s.charCodeAt(i) - 48); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for (i = 1; i < s.length; i++) num = num * 10 + (s.charCodeAt(i) - 48); num = num * -1; } return num; } // This function receives a node of the syntax // tree and recursively evaluate it function evalTree(root) { // Empty tree if (root == null) return 0; // Leaf node i.e an integer if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return toInt(root.data); // Evaluate left subtree var leftEval = evalTree(root.left); // Evaluate right subtree var rightEval = evalTree(root.right); // Check which operator to apply if (root.data === ('+')) return leftEval + rightEval; if (root.data === ('-')) return leftEval - rightEval; if (root.data === ('*')) return leftEval * rightEval; return leftEval / rightEval; } // Driver code // Creating a sample tree var root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('-4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('20'); document.write(evalTree(root)); root = null; // Creating a sample tree root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('/'); root.right.right.left = new Node('20'); root.right.right.right = new Node('2'); document.write('
'+evalTree(root)); // This code is contributed by gauravrajput1 </script>
Producción
60 110
Complejidad del tiempo: O(n) ya que cada nodo se visita una vez.
Espacio Auxiliar: En)