Los bucles en programación se utilizan para repetir un bloque de código hasta que se cumpla la condición especificada. Una declaración de bucle permite a los programadores ejecutar una declaración o un grupo de declaraciones varias veces sin repetición de código.
subprograma
C
programación cobol
// C program to illustrate need of loops> #include> > int> main()> {> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> > >return> 0;> }> |
>
álgebra de conjuntos
>Producción
Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World>
Existen principalmente dos tipos de bucles en programación C:
cadena en int
- Bucles controlados de entrada: en los bucles controlados de entrada, la condición de prueba se verifica antes de ingresar al cuerpo principal del bucle. Bucle For y bucle While son bucles controlados por entrada. Bucles de salida controlada: en los bucles de salida controlada, la condición de prueba se evalúa al final del cuerpo del bucle. El cuerpo del bucle se ejecutará al menos una vez, independientemente de si la condición es verdadera o falsa. bucle hacer-mientras es un bucle controlado de salida.
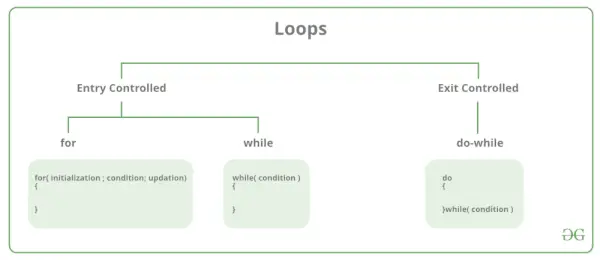
| Tipo de bucle | Descripción |
|---|---|
| en bucle | Primero se inicializa, luego se verifica la condición, luego se ejecuta el cuerpo y, por último, se realiza la actualización. |
| mientras bucle | Primero inicializa, luego verifica las condiciones y luego ejecuta el cuerpo, y la actualización puede realizarse dentro del cuerpo. |
| bucle hacer-mientras | do- while primero ejecuta el cuerpo y luego se realiza la verificación de condición. |
en bucle
El bucle for en programación C es una estructura de control de repetición que permite a los programadores escribir un bucle que se ejecutará un número específico de veces. El bucle for permite a los programadores realizar n números de pasos juntos en una sola línea.
Sintaxis:
for (initialize expression; test expression; update expression) { // // body of for loop // }> Ejemplo:
for(int i = 0; i In for loop, a loop variable is used to control the loop. Firstly we initialize the loop variable with some value, then check its test condition. If the statement is true then control will move to the body and the body of for loop will be executed. Steps will be repeated till the exit condition becomes true. If the test condition will be false then it will stop. Initialization Expression: In this expression, we assign a loop variable or loop counter to some value. for example: int i=1; Test Expression: In this expression, test conditions are performed. If the condition evaluates to true then the loop body will be executed and then an update of the loop variable is done. If the test expression becomes false then the control will exit from the loop. for example, i<=9; Update Expression: After execution of the loop body loop variable is updated by some value it could be incremented, decremented, multiplied, or divided by any value. for loop Equivalent Flow Diagram: Example: C // C program to illustrate for loop #include // Driver code int main() { int i = 0; for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { printf( 'Hello World
'); } return 0; } Output Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World While Loop While loop does not depend upon the number of iterations. In for loop the number of iterations was previously known to us but in the While loop, the execution is terminated on the basis of the test condition. If the test condition will become false then it will break from the while loop else body will be executed. Syntax: initialization_expression; while (test_expression) { // body of the while loop update_expression; } Flow Diagram for while loop: C // C program to illustrate // while loop #include // Driver code int main() { // Initialization expression int i = 2; // Test expression while(i <10) { // loop body printf( 'Hello World
'); // update expression i++; } return 0; } Output Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World do-while Loop The do-while loop is similar to a while loop but the only difference lies in the do-while loop test condition which is tested at the end of the body. In the do-while loop, the loop body will execute at least once irrespective of the test condition. Syntax: initialization_expression; do { // body of do-while loop update_expression; } while (test_expression); C // C program to illustrate // do-while loop #include // Driver code int main() { // Initialization expression int i = 2; do { // loop body printf( 'Hello World
'); // Update expression i++; // Test expression } while (i <1); return 0; } Output Hello World Above program will evaluate (i<1) as false since i = 2. But still, as it is a do-while loop the body will be executed once. Loop Control Statements Loop control statements in C programming are used to change execution from its normal sequence. Name Description break statement the break statement is used to terminate the switch and loop statement. It transfers the execution to the statement immediately following the loop or switch. continue statement continue statement skips the remainder body and immediately resets its condition before reiterating it. goto statement goto statement transfers the control to the labeled statement. Infinite Loop An infinite loop is executed when the test expression never becomes false and the body of the loop is executed repeatedly. A program is stuck in an Infinite loop when the condition is always true. Mostly this is an error that can be resolved by using Loop Control statements. Using for loop: C // C program to demonstrate infinite // loops using for loop #include // Driver code int main () { int i; // This is an infinite for loop // as the condition expression // is blank for ( ; ; ) { printf('This loop will run forever.
'); } return 0; } Output This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. ... Using While loop: C // C program to demonstrate // infinite loop using while // loop #include // Driver code int main() { while (1) printf('This loop will run forever.
'); return 0; } Output This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. ... Using the do-while loop: C // C program to demonstrate // infinite loop using do-while // loop #include // Driver code int main() { do { printf('This loop will run forever.
'); } while (1); return 0; } Output This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. ...>