El comoLista() método de java.util.Arrays La clase se utiliza para devolver una lista de tamaño fijo respaldada por la matriz especificada. Este método actúa como un puente entre las API basadas en matrices y basadas en colecciones , en combinación con Collection.toArray(). La lista devuelta es serializable e implementa RandomAccess.
Consejo: Esto se ejecuta en tiempo O(1).
Sintaxis:
public static List asList(T... a)>
Parámetros: Este método toma la matriz un que debe convertirse en una Lista. Aquí… se le conoce como Vararg que es una matriz de parámetros y funciona de manera similar a un parámetro de matriz de objetos.
Nota especial: El tipo de matriz debe ser una clase contenedora (Entero, Flotante, etc.) en el caso de tipos de datos primitivos (int, flotante, etc.), es decir, no puede pasar int a[] pero puede pasar Integer a[]. Si pasa int a[], esta función devolverá una Lista y no una Lista, ya que el autoboxing no ocurre en este caso e int a[] se identifica como un objeto y se devuelve una Lista de matriz int, en lugar de una lista. de números enteros, lo que dará error en varias funciones de Colección.
ls comandos linux
Valor de retorno: Este método devuelve un vista de la lista de la matriz especificada.
Ejemplo 1:
Java
llave de inserción del ordenador portátil
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class for a string value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of String type> >String a[]> >=>new> String[] {>'A'>,>'B'>,>'C'>,>'D'> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements in list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statement> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>
funciones de cadena en javaProducción
The list is: [A, B, C, D]>
Ejemplo 2:
Java
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class For an integer value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements inside list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statements> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>
iterar a través del mapa javaProducción
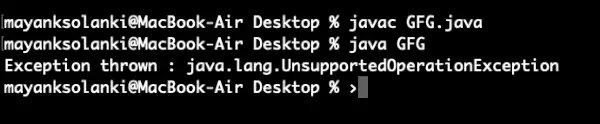
The list is: [10, 20, 30, 40]>
Ejemplo 3:
Java
alinear imágenes en css
// Java Program to demonstrate asList() method> // Which returns fixed size list and> // throws UnsupportedOperationException> // if any element is added using add() method> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Adding another int to the list> >// As Arrays.asList() returns fixed size> >// list, we'll get> >// java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException> >list.add(>50>);> >// Printing all the elements of list> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (UnsupportedOperationException e) {> >// Display message when exception occurs> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>
Producción: