En esta sección aprenderemos ¿Qué es un número espía? y también crear programas java para comprobar si el número dado es Espiar O no. El programa de numero espia se pregunta frecuentemente en Java prueba de codificación.
Número espía
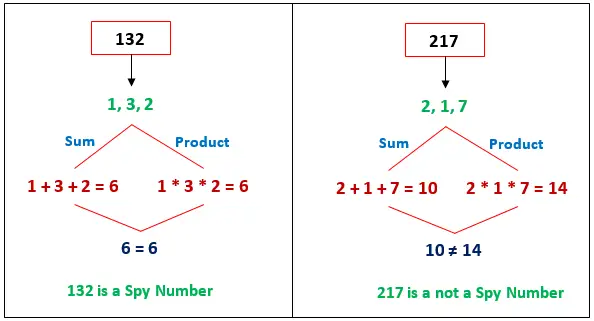
Un número entero positivo se llama número espía si el suma y producto de sus dígitos son iguales. En otras palabras, un número cuya suma y producto de todos los dígitos son iguales se llama número espía .
Ejemplo de número espía
Tomemos el número 1124 y comprobemos si es un número espía o no. Primero, lo dividiremos en dígitos (1, 1, 2, 4). Después de eso encuentra la suma y el producto de todos los dígitos.
Suma =1+1+2+4= 8
Producto =1*1*2*4= 8
Observamos que la suma y el producto de los dígitos son iguales. Por eso, 1124 Es un número espía.
Del mismo modo, también podemos consultar otros números. Algunos otros números espía son 22, 123, 132, etc.
Pasos para encontrar el número espía
- Leer o inicializar un número ( norte ) que desea comprobar.
- Declarar dos variables suma y producto para almacenar suma y producto de dígitos. Inicializar suma con 0 y producto con 1 .
- Encuentra el último dígito (n%10) del número dado utilizando el operador de módulo.
- Repita los pasos 3 a 6 hasta que el número dado (n) se convierta en 0.
- Si la variable suma y producto tienen el mismo valor, entonces el número dado (n) es un espiar número , de lo contrario no es un número espía.
Implementemos los pasos anteriores en un programa Java.
Programa Java de número espía
SpyNumberExample1.java
import java.util.Scanner; public class SpyNumberExample1 { public static void main(String args[]) { int num, product=1, sum=0, lastdigit; // create object of scanner Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter the number to check: ' ); //reads an integer from the user and stores it in the variable num num=sc.nextInt(); //executes untill the condition becomes false while(num>0) { //finds the last digit of the number lastdigit=num%10; //adds last digit to the variable sum sum=sum+lastdigit; //calculates the product product=product*lastdigit; //removes the last digit from the given number num=num/10; } //compares the sum and product if(sum==product) //prints if the above condition returns true System.out.println('The given number is a spy number.'); else //prints if the above condition returns false System.out.println('The given number is not a spy number.'); } } Salida 1:
Enter the number to check: 123 The given number is a spy number.
Salida 2:
Enter the number to check: 456 The given number is a not spy number.
SpyNumberExample2.java
import java.util.Scanner; public class SpyNumberExample2 { //method to check the Spy number private static boolean isSpyNumber(int number) { int lastDigit = 0; int sum = 0; int product = 1; //executes until the condition returns true while(number != 0) { //determines the last digit of the given number lastDigit = number % 10; //adds the last digit to the variable sum sum = sum + lastDigit; //multiply last digit with product product = product * lastDigit; //removes the last digit of the given number number = number / 10; } //compares the variable sum with product and returns the result accordingly if(sum == product) return true; return false; } //driver code public static void main(String args[]) { int lowerRange = 0, upperRange = 0; Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter the lower range: '); //reads lower range lowerRange = sc.nextInt(); System.out.print('Enter upper range: '); //reads the upper range upperRange = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println('The Spy numbers between '+ lowerRange + ' to '+ upperRange+' are: '); for(int i=lowerRange; i<=upperrange; i++) { calling user-defined function that checks if the given number is spy or not if(isspynumber(i)) prints all numbers system.out.print(i +' '); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter the lower range: 1 Enter upper range: 10000 The Spy numbers between 1 to 10000 are: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 22 123 132 213 231 312 321 1124 1142 1214 1241 1412 1421 2114 2141 2411 4112 4121 4211 </pre> <hr></=upperrange;> 