Dado un papel rectangular de dimensiones a x b . La tarea es cortar todo el papel en el mínimo numero de cuadrado piezas. Podemos elegir piezas cuadradas de cualquier tamaño pero hay que cortarlas. sin superponerse ni dejar espacio extra .
Ejemplos:
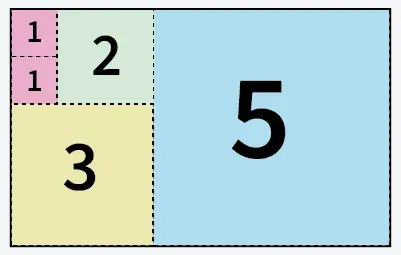
Aporte: a = 5 b = 8
5 cuadrados cortados de papel de tamaño 5 X 8
Producción: 5
Explicación: Podemos cortar el papel en 5 cuadrados: 1 cuadrado de tamaño 5x5 1 cuadrado de tamaño 3x3 1 cuadrado de tamaño 2x2 y 2 cuadrados de tamaño 1x1.Aporte: a = 13 b = 11
6 cuadrados cortados de papel de tamaño 13 X 11
Producción: 6
Explicación: Podemos cortar el papel en 6 cuadrados: 1 cuadrado de tamaño 7x7 1 cuadrado de tamaño 6x6 1 cuadrado de tamaño 5x5 2 cuadrados de tamaño 4x4 y 1 cuadrado de tamaño 1x1.ejemplos de programación en PythonAporte: a = 6 b = 7
5 cuadrados cortados de papel de tamaño 6 X 7
Producción: 5
Explicación: Podemos cortar el papel en 5 cuadrados: 1 cuadrado de tamaño 4x4 2 cuadrados de tamaño 3x3 y 2 cuadrados de tamaño 3x3.
Tabla de contenido
- [Enfoque incorrecto 1] Uso de la técnica codiciosa
- [Enfoque incorrecto 2] Uso de la programación dinámica
- [Enfoque correcto] Uso de DFS y programación dinámica
[Enfoque incorrecto 1] Uso de la técnica codiciosa
A primera vista, podría parecer que el problema se puede resolver fácilmente cortando primero el cuadrado más grande posible del papel, luego cortando el cuadrado más grande del papel restante y así sucesivamente hasta que hayamos cortado todo el papel. Pero esta solución es incorrecta.
¿Por qué el enfoque codicioso no funciona?
estado de gitConsidere un papel de tamaño 6x7 entonces si intentamos cortar el papel con avidez obtendremos 7 cuadrícula: 1 cuadrado de tamaño 6x6 y 6 cuadrados de tamaño 1x1 mientras que la solución correcta es: 5. Por lo tanto, el enfoque codicioso no funcionará.
[Enfoque incorrecto 2] Uso de la programación dinámica
Programación dinámica con cortes verticales u horizontales: Otra solución que podría parecer correcta es utilizar Programación dinámica . Podemos mantener una tabla dp[][] tal que dp[i][j] = número mínimo de cuadrados que se pueden cortar de papel de tamaño yo x j . Luego para papel de tamaño axb
- Podemos intentar cortarlo a lo largo de cada fila: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) donde k puede estar en el rango [1 i - 1].
- Podemos intentar cortarlo a lo largo de cada columna: dp[i][j] = mín(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) donde k puede estar en el rango [1 j - 1].
Finalmente, un mínimo de todos los recortes será la respuesta. Pero esta solución también es incorrecta.
¿Por qué no funciona cortar vertical u horizontalmente con el enfoque de programación dinámica?
Esto no funcionará porque suponemos que un corte vertical u horizontal siempre dividirá el rectángulo en dos partes. Considere un papel de tamaño 13x11 luego, si intentamos cortar el papel usando el método DP, obtendremos 8 cuadrados, pero la respuesta correcta (como se muestra en los ejemplos) es 6. Por lo tanto, la programación dinámica no funcionará.
[Enfoque correcto] Uso de DFS y programación dinámica
C++El idea es cortar todo el papel usando DFS en de abajo hacia arriba manera. En cada paso, busque la esquina inferior izquierda del papel e intente cortar cuadrados de todos los tamaños posibles desde esa esquina. Después de cortar un cuadrado nuevamente, busque la esquina inferior izquierda del papel restante para cortar cuadrados de todos los tamaños posibles, y así sucesivamente. Pero si intentamos realizar todos los cortes posibles desde la esquina inferior izquierda de cada tamaño de papel posible, sería bastante ineficiente. Podemos optimizarlo usando Programación dinámica para almacenar cortes mínimos para cada tamaño de papel posible.
Para identificar de forma única cualquier tamaño de papel, podemos mantener una matriz remSq[] de modo que remSq[i] almacene el número de cuadrados restantes de tamaño 1x1 en la iésima columna del papel. Entonces, para un papel de tamaño 6x7 remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. Además, para encontrar la esquina inferior izquierda encontraremos el primer índice que tenga el máximo de cuadrados restantes. Entonces podemos aplicar un hash al valor de la matriz remSq[] para encontrar una clave única para todos los valores posibles de la matriz remSq[].
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include
// Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.*; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int base = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Map<Integer Integer> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key); int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = Arrays.copyOf(remSq b); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo.put(key ans); return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; Arrays.fill(remSq a); Map<Integer Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System.out.println(minCut(a b)); } }
# Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey(remSq b): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range(b): key += remSq[i] * base base = base * (b + 1) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil(remSq a b memo): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey(remSq b) if key in memo: return memo[key] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range(b): if remSq[i] > maxRemSq: maxRemSq = remSq[i] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0: return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq[:] ans = float('inf') # Find the ending point of min height while end < b: # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq or newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0: break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range(start end + 1): newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)) end += 1 memo[key] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut(a b): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b: return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [a] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print(minCut(a b))
// C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int baseVal = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * baseVal); baseVal = baseVal * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Dictionary<int int> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.ContainsKey(key)) return memo[key]; int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = (int[])remSq.Clone(); int ans = int.MaxValue; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.Min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) remSq[i] = a; Dictionary<int int> memo = new Dictionary<int int>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } static void Main() { int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console.WriteLine(minCut(a b)); } }
// JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey(remSq b) { let base = 1; let key = 0; for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey(remSq b); if (key in memo) return memo[key]; let maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq === 0) return 0; end = start; let newRemSq = remSq.slice(); let ans = Infinity; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut(a b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a === b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array(b).fill(a); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console.log(minCut(a b));
Producción
6
Complejidad del tiempo: O(a^b) para cada una de las b columnas podemos tener cuadrados.
Espacio auxiliar: O(a^b) debido a la memorización que almacena cada estado único.

 5 cuadrados cortados de papel de tamaño 5 X 8
5 cuadrados cortados de papel de tamaño 5 X 8 6 cuadrados cortados de papel de tamaño 13 X 11
6 cuadrados cortados de papel de tamaño 13 X 11 5 cuadrados cortados de papel de tamaño 6 X 7
5 cuadrados cortados de papel de tamaño 6 X 7