Combinar ordenar es un algoritmo de clasificación que sigue el divide y conquistaras acercarse. Funciona dividiendo recursivamente la matriz de entrada en subarreglos más pequeños y ordenándolos y luego fusionándolos nuevamente para obtener el arreglo ordenado.
conversión de cadena java a int
En términos simples, podemos decir que el proceso de fusionar ordenar es dividir la matriz en dos mitades, ordenar cada mitad y luego fusionar las mitades ordenadas nuevamente. Este proceso se repite hasta que se ordena toda la matriz.
Algoritmo de clasificación por fusión
¿Cómo funciona Combinar ordenación?
Merge sort es un algoritmo de clasificación popular conocido por su eficiencia y estabilidad. Sigue el divide y conquistaras método para ordenar una determinada matriz de elementos.
Aquí hay una explicación paso a paso de cómo funciona la ordenación por combinación:
- Dividir: Divida la lista o matriz de forma recursiva en dos mitades hasta que ya no se pueda dividir.
- Conquistar: Cada subarreglo se ordena individualmente mediante el algoritmo de ordenación por combinación.
- Unir: Los subarreglos ordenados se vuelven a fusionar en orden ordenado. El proceso continúa hasta que se hayan fusionado todos los elementos de ambos subarreglos.
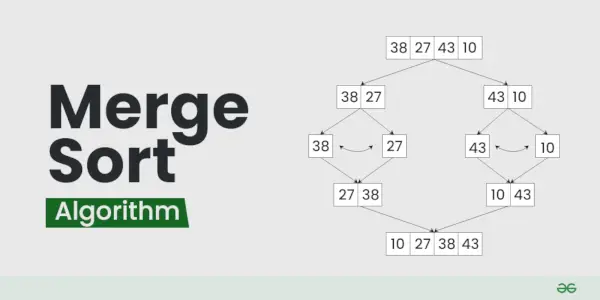
Ilustración de ordenación por combinación:
Ordenemos la matriz o lista [38, 27, 43, 10] usando Combinar Ordenar
Práctica recomendada ¡Pruébelo!Veamos el funcionamiento del ejemplo anterior:
Dividir:
- [38, 27, 43, 10] se divide en [38, 27 ] y [43, 10] .
- [38, 27] se divide en [38] y [27] .
- [43, 10] se divide en [43] y [10] .
Conquistar:
- [38] ya está ordenado.
- [27] ya está ordenado.
- [43] ya está ordenado.
- [10] ya está ordenado.
Unir:
- Unir [38] y [27] Llegar [27, 38] .
- Unir [43] y [10] Llegar [10,43] .
- Unir [27, 38] y [10,43] para obtener la lista final ordenada [10, 27, 38, 43]
Por lo tanto, la lista ordenada es [10, 27, 38, 43] .
cómo convertir un número entero a una cadena java
Implementación de Merge Sort:
C++ // C++ program for Merge Sort #include using namespace std; // Merges two subarrays of array[]. // First subarray is arr[begin..mid] // Second subarray is arr[mid+1..end] void merge(int array[], int const left, int const mid, int const right) { int const subArrayOne = mid - left + 1; int const subArrayTwo = right - mid; // Create temp arrays auto *leftArray = new int[subArrayOne], *rightArray = new int[subArrayTwo]; // Copy data to temp arrays leftArray[] and rightArray[] for (auto i = 0; i < subArrayOne; i++) leftArray[i] = array[left + i]; for (auto j = 0; j < subArrayTwo; j++) rightArray[j] = array[mid + 1 + j]; auto indexOfSubArrayOne = 0, indexOfSubArrayTwo = 0; int indexOfMergedArray = left; // Merge the temp arrays back into array[left..right] while (indexOfSubArrayOne < subArrayOne && indexOfSubArrayTwo < subArrayTwo) { if (leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne] <= rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo]) { array[indexOfMergedArray] = leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne]; indexOfSubArrayOne++; } else { array[indexOfMergedArray] = rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo]; indexOfSubArrayTwo++; } indexOfMergedArray++; } // Copy the remaining elements of // left[], if there are any while (indexOfSubArrayOne < subArrayOne) { array[indexOfMergedArray] = leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne]; indexOfSubArrayOne++; indexOfMergedArray++; } // Copy the remaining elements of // right[], if there are any while (indexOfSubArrayTwo < subArrayTwo) { array[indexOfMergedArray] = rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo]; indexOfSubArrayTwo++; indexOfMergedArray++; } delete[] leftArray; delete[] rightArray; } // begin is for left index and end is right index // of the sub-array of arr to be sorted void mergeSort(int array[], int const begin, int const end) { if (begin>= fin) regresar; int mid = comienzo + (fin - comienzo) / 2; mergeSort(matriz, comienzo, mitad); mergeSort(matriz, mitad + 1, final); fusionar (matriz, comienzo, mitad, final); } // FUNCIONES DE UTILIDAD // Función para imprimir una matriz void printArray(int A[], int size) { for (int i = 0; i< size; i++) cout << A[i] << ' '; cout << endl; } // Driver code int main() { int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 }; int arr_size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); cout << 'Given array is
'; printArray(arr, arr_size); mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1); cout << '
Sorted array is
'; printArray(arr, arr_size); return 0; } // This code is contributed by Mayank Tyagi // This code was revised by Joshua Estes> C // C program for Merge Sort #include #include // Merges two subarrays of arr[]. // First subarray is arr[l..m] // Second subarray is arr[m+1..r] void merge(int arr[], int l, int m, int r) { int i, j, k; int n1 = m - l + 1; int n2 = r - m; // Create temp arrays int L[n1], R[n2]; // Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[] for (i = 0; i < n1; i++) L[i] = arr[l + i]; for (j = 0; j < n2; j++) R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j]; // Merge the temp arrays back into arr[l..r i = 0; j = 0; k = l; while (i < n1 && j < n2) { if (L[i] <= R[j]) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; } else { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; } k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of L[], // if there are any while (i < n1) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of R[], // if there are any while (j < n2) { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; k++; } } // l is for left index and r is right index of the // sub-array of arr to be sorted void mergeSort(int arr[], int l, int r) { if (l < r) { int m = l + (r - l) / 2; // Sort first and second halves mergeSort(arr, l, m); mergeSort(arr, m + 1, r); merge(arr, l, m, r); } } // Function to print an array void printArray(int A[], int size) { int i; for (i = 0; i < size; i++) printf('%d ', A[i]); printf('
'); } // Driver code int main() { int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 }; int arr_size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); printf('Given array is
'); printArray(arr, arr_size); mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1); printf('
Sorted array is
'); printArray(arr, arr_size); return 0; }> Java // Java program for Merge Sort import java.io.*; class MergeSort { // Merges two subarrays of arr[]. // First subarray is arr[l..m] // Second subarray is arr[m+1..r] void merge(int arr[], int l, int m, int r) { // Find sizes of two subarrays to be merged int n1 = m - l + 1; int n2 = r - m; // Create temp arrays int L[] = new int[n1]; int R[] = new int[n2]; // Copy data to temp arrays for (int i = 0; i < n1; ++i) L[i] = arr[l + i]; for (int j = 0; j < n2; ++j) R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j]; // Merge the temp arrays // Initial indices of first and second subarrays int i = 0, j = 0; // Initial index of merged subarray array int k = l; while (i < n1 && j < n2) { if (L[i] <= R[j]) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; } else { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; } k++; } // Copy remaining elements of L[] if any while (i < n1) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; k++; } // Copy remaining elements of R[] if any while (j < n2) { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; k++; } } // Main function that sorts arr[l..r] using // merge() void sort(int arr[], int l, int r) { if (l < r) { // Find the middle point int m = l + (r - l) / 2; // Sort first and second halves sort(arr, l, m); sort(arr, m + 1, r); // Merge the sorted halves merge(arr, l, m, r); } } // A utility function to print array of size n static void printArray(int arr[]) { int n = arr.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) System.out.print(arr[i] + ' '); System.out.println(); } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 }; System.out.println('Given array is'); printArray(arr); MergeSort ob = new MergeSort(); ob.sort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1); System.out.println('
Sorted array is'); printArray(arr); } } /* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */> Pitón # Merges two subarrays of array[]. # First subarray is arr[left..mid] # Second subarray is arr[mid+1..right] def merge(array, left, mid, right): subArrayOne = mid - left + 1 subArrayTwo = right - mid # Create temp arrays leftArray = [0] * subArrayOne rightArray = [0] * subArrayTwo # Copy data to temp arrays leftArray[] and rightArray[] for i in range(subArrayOne): leftArray[i] = array[left + i] for j in range(subArrayTwo): rightArray[j] = array[mid + 1 + j] indexOfSubArrayOne = 0 # Initial index of first sub-array indexOfSubArrayTwo = 0 # Initial index of second sub-array indexOfMergedArray = left # Initial index of merged array # Merge the temp arrays back into array[left..right] while indexOfSubArrayOne < subArrayOne and indexOfSubArrayTwo < subArrayTwo: if leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne] <= rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo]: array[indexOfMergedArray] = leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne] indexOfSubArrayOne += 1 else: array[indexOfMergedArray] = rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo] indexOfSubArrayTwo += 1 indexOfMergedArray += 1 # Copy the remaining elements of left[], if any while indexOfSubArrayOne < subArrayOne: array[indexOfMergedArray] = leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne] indexOfSubArrayOne += 1 indexOfMergedArray += 1 # Copy the remaining elements of right[], if any while indexOfSubArrayTwo < subArrayTwo: array[indexOfMergedArray] = rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo] indexOfSubArrayTwo += 1 indexOfMergedArray += 1 # begin is for left index and end is right index # of the sub-array of arr to be sorted def mergeSort(array, begin, end): if begin>= fin: return mid = comienzo + (fin - comienzo) // 2 mergeSort(array, start, mid) mergeSort(array, mid + 1, end) merge(array, start, mid, end) # Función para imprimir una matriz def printArray(matriz, tamaño): for i in range(size): print(array[i], end=' ') print() # Código del controlador if __name__ == '__main__': arr = [12 , 11, 13, 5, 6, 7] arr_size = len(arr) print('La matriz dada es') printArray(arr, arr_size) mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1) print('
Matriz ordenada es') printArray(arr, arr_size)> C# // C# program for Merge Sort using System; class MergeSort { // Merges two subarrays of []arr. // First subarray is arr[l..m] // Second subarray is arr[m+1..r] void merge(int[] arr, int l, int m, int r) { // Find sizes of two // subarrays to be merged int n1 = m - l + 1; int n2 = r - m; // Create temp arrays int[] L = new int[n1]; int[] R = new int[n2]; int i, j; // Copy data to temp arrays for (i = 0; i < n1; ++i) L[i] = arr[l + i]; for (j = 0; j < n2; ++j) R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j]; // Merge the temp arrays // Initial indexes of first // and second subarrays i = 0; j = 0; // Initial index of merged // subarray array int k = l; while (i < n1 && j < n2) { if (L[i] <= R[j]) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; } else { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; } k++; } // Copy remaining elements // of L[] if any while (i < n1) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; k++; } // Copy remaining elements // of R[] if any while (j < n2) { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; k++; } } // Main function that // sorts arr[l..r] using // merge() void sort(int[] arr, int l, int r) { if (l < r) { // Find the middle point int m = l + (r - l) / 2; // Sort first and second halves sort(arr, l, m); sort(arr, m + 1, r); // Merge the sorted halves merge(arr, l, m, r); } } // A utility function to // print array of size n static void printArray(int[] arr) { int n = arr.Length; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) Console.Write(arr[i] + ' '); Console.WriteLine(); } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { int[] arr = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 }; Console.WriteLine('Given array is'); printArray(arr); MergeSort ob = new MergeSort(); ob.sort(arr, 0, arr.Length - 1); Console.WriteLine('
Sorted array is'); printArray(arr); } } // This code is contributed by Princi Singh> JavaScript // JavaScript program for Merge Sort // Merges two subarrays of arr[]. // First subarray is arr[l..m] // Second subarray is arr[m+1..r] function merge(arr, l, m, r) { var n1 = m - l + 1; var n2 = r - m; // Create temp arrays var L = new Array(n1); var R = new Array(n2); // Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[] for (var i = 0; i < n1; i++) L[i] = arr[l + i]; for (var j = 0; j < n2; j++) R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j]; // Merge the temp arrays back into arr[l..r] // Initial index of first subarray var i = 0; // Initial index of second subarray var j = 0; // Initial index of merged subarray var k = l; while (i < n1 && j < n2) { if (L[i] <= R[j]) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; } else { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; } k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of // L[], if there are any while (i < n1) { arr[k] = L[i]; i++; k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of // R[], if there are any while (j < n2) { arr[k] = R[j]; j++; k++; } } // l is for left index and r is // right index of the sub-array // of arr to be sorted function mergeSort(arr,l, r){ if(l>=r){ retorno; } var m =l+ parseInt((r-l)/2); fusionarOrdenar(arr,l,m); fusionarOrdenar(arr,m+1,r); fusionar(arr,l,m,r); } // Función para imprimir una función de matriz printArray( A, tamaño) { for (var i = 0; i< size; i++) console.log( A[i] + ' '); } var arr = [ 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 ]; var arr_size = arr.length; console.log( 'Given array is '); printArray(arr, arr_size); mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1); console.log( 'Sorted array is '); printArray(arr, arr_size); // This code is contributed by SoumikMondal> PHP /* PHP recursive program for Merge Sort */ // Merges two subarrays of arr[]. // First subarray is arr[l..m] // Second subarray is arr[m+1..r] function merge(&$arr, $l, $m, $r) { $n1 = $m - $l + 1; $n2 = $r - $m; // Create temp arrays $L = array(); $R = array(); // Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[] for ($i = 0; $i < $n1; $i++) $L[$i] = $arr[$l + $i]; for ($j = 0; $j < $n2; $j++) $R[$j] = $arr[$m + 1 + $j]; // Merge the temp arrays back into arr[l..r] $i = 0; $j = 0; $k = $l; while ($i < $n1 && $j < $n2) { if ($L[$i] <= $R[$j]) { $arr[$k] = $L[$i]; $i++; } else { $arr[$k] = $R[$j]; $j++; } $k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of L[], // if there are any while ($i < $n1) { $arr[$k] = $L[$i]; $i++; $k++; } // Copy the remaining elements of R[], // if there are any while ($j < $n2) { $arr[$k] = $R[$j]; $j++; $k++; } } // l is for left index and r is right index of the // sub-array of arr to be sorted function mergeSort(&$arr, $l, $r) { if ($l < $r) { $m = $l + (int)(($r - $l) / 2); // Sort first and second halves mergeSort($arr, $l, $m); mergeSort($arr, $m + 1, $r); merge($arr, $l, $m, $r); } } // Function to print an array function printArray($A, $size) { for ($i = 0; $i < $size; $i++) echo $A[$i].' '; echo '
'; } // Driver code $arr = array(12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7); $arr_size = sizeof($arr); echo 'Given array is
'; printArray($arr, $arr_size); mergeSort($arr, 0, $arr_size - 1); echo '
Sorted array is
'; printArray($arr, $arr_size); return 0; //This code is contributed by Susobhan Akhuli ?>> Producción
Given array is 12 11 13 5 6 7 Sorted array is 5 6 7 11 12 13>
Análisis de complejidad de la ordenación por combinación:
Complejidad del tiempo:
- Mejor caso: O (n log n), cuando la matriz ya está ordenada o casi ordenada.
- Caso promedio: O (n log n), cuando la matriz está ordenada aleatoriamente.
- Peor de los casos: O (n log n), cuando la matriz se ordena en orden inverso.
Complejidad espacial: O(n), se requiere espacio adicional para la matriz temporal utilizada durante la fusión.
Ventajas de ordenar por combinación:
- Estabilidad : Merge sort es un algoritmo de clasificación estable, lo que significa que mantiene el orden relativo de elementos iguales en la matriz de entrada.
- Rendimiento garantizado en el peor de los casos: La clasificación por combinación tiene una complejidad temporal en el peor de los casos de O(N iniciar sesiónN) , lo que significa que funciona bien incluso en grandes conjuntos de datos.
- Sencillo de implementar: El enfoque de divide y vencerás es sencillo.
Desventaja de la ordenación por combinación:
- Complejidad espacial: La clasificación por combinación requiere memoria adicional para almacenar los subarreglos combinados durante el proceso de clasificación.
- Fuera de lugar: La clasificación por combinación no es un algoritmo de clasificación local, lo que significa que requiere memoria adicional para almacenar los datos ordenados. Esto puede ser una desventaja en aplicaciones donde el uso de memoria es una preocupación.
Aplicaciones de Merge Sort:
- Ordenar grandes conjuntos de datos
- Clasificación externa (cuando el conjunto de datos es demasiado grande para caber en la memoria)
- Conteo de inversiones (contando el número de inversiones en una matriz)
- Encontrar la mediana de una matriz
Enlaces rápidos:
- Artículos recientes sobre ordenación por combinación
- Clasificación de preguntas y problemas principales de la entrevista
- Problemas de práctica sobre el algoritmo de clasificación.
- Prueba sobre ordenación por fusión
