 #practiceLinkDiv { mostrar: ninguno !importante; }
#practiceLinkDiv { mostrar: ninguno !importante; }Dado un árbol binario, encuentre la longitud de la ruta más larga que se compone de nodos con valores consecutivos en orden creciente. Cada nodo se considera un camino de longitud 1.
Ejemplos:
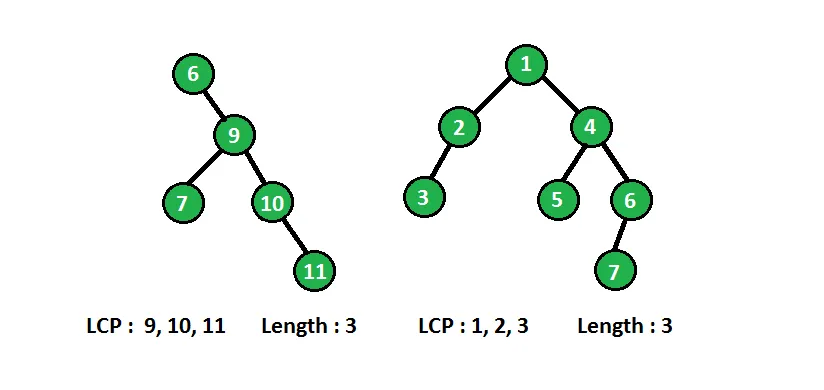
In below diagram binary tree with longest consecutive path(LCP) are shown :
Podemos resolver el problema anterior de forma recursiva. En cada nodo necesitamos información de su nodo principal. Si el nodo actual tiene un valor uno más que su nodo principal, entonces crea una ruta consecutiva en cada nodo, compararemos el valor del nodo con su valor principal y actualizaremos la ruta consecutiva más larga en consecuencia.
Para obtener el valor del nodo principal, pasaremos (valor_nodo + 1) como argumento al método recursivo y compararemos el valor del nodo con este valor de argumento si satisface la actualización de la longitud actual de la ruta consecutiva; de lo contrario, reinicializaremos la longitud de la ruta actual en 1.
Consulte el código a continuación para una mejor comprensión:
C++// C/C++ program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree #include
// Java program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class Result { int res = 0; } class BinaryTree { Node root; // method returns length of longest consecutive // sequence rooted at node root int longestConsecutive(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; Result res = new Result(); // call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res); return res.res; } // Utility method to return length of longest // consecutive sequence of tree private void longestConsecutiveUtil(Node root int curlength int expected Result res) { if (root == null) return; // if root data has one more than its parent // then increase current length if (root.data == expected) curlength++; else curlength = 1; // update the maximum by current length res.res = Math.max(res.res curlength); // recursively call left and right subtree with // expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curlength root.data + 1 res); longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curlength root.data + 1 res); } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); tree.root = new Node(6); tree.root.right = new Node(9); tree.root.right.left = new Node(7); tree.root.right.right = new Node(10); tree.root.right.right.right = new Node(11); System.out.println(tree.longestConsecutive(tree.root)); } } // This code is contributed by shubham96301
# Python3 program to find longest consecutive # sequence in binary tree # A utility class to create a node class newNode: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.left = self.right = None # Utility method to return length of # longest consecutive sequence of tree def longestConsecutiveUtil(root curLength expected res): if (root == None): return # if root data has one more than its # parent then increase current length if (root.data == expected): curLength += 1 else: curLength = 1 # update the maximum by current length res[0] = max(res[0] curLength) # recursively call left and right subtree # with expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curLength root.data + 1 res) longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curLength root.data + 1 res) # method returns length of longest consecutive # sequence rooted at node root def longestConsecutive(root): if (root == None): return 0 res = [0] # call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res) return res[0] # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': root = newNode(6) root.right = newNode(9) root.right.left = newNode(7) root.right.right = newNode(10) root.right.right.right = newNode(11) print(longestConsecutive(root)) # This code is contributed by PranchalK
// C# program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class Result { public int res = 0; } class GFG { Node root; // method returns length of longest consecutive // sequence rooted at node root int longestConsecutive(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; Result res = new Result(); // call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res); return res.res; } // Utility method to return length of longest // consecutive sequence of tree private void longestConsecutiveUtil(Node root int curlength int expected Result res) { if (root == null) return; // if root data has one more than its parent // then increase current length if (root.data == expected) curlength++; else curlength = 1; // update the maximum by current length res.res = Math.Max(res.res curlength); // recursively call left and right subtree with // expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curlength root.data + 1 res); longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curlength root.data + 1 res); } // Driver code public static void Main(String []args) { GFG tree = new GFG(); tree.root = new Node(6); tree.root.right = new Node(9); tree.root.right.left = new Node(7); tree.root.right.right = new Node(10); tree.root.right.right.right = new Node(11); Console.WriteLine(tree.longestConsecutive(tree.root)); } } // This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
<script> // JavaScript program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree class Node { constructor(item) { this.data=item; this.left = this.right = null; } } let res = 0; let root; function longestConsecutive(root) { if (root == null) return 0; res=[0]; // call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res); return res[0]; } // Utility method to return length of longest // consecutive sequence of tree function longestConsecutiveUtil(rootcurlength expectedres) { if (root == null) return; // if root data has one more than its parent // then increase current length if (root.data == expected) curlength++; else curlength = 1; // update the maximum by current length res[0] = Math.max(res[0] curlength); // recursively call left and right subtree with // expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curlength root.data + 1 res); longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curlength root.data + 1 res); } // Driver code root = new Node(6); root.right = new Node(9); root.right.left = new Node(7); root.right.right = new Node(10); root.right.right.right = new Node(11); document.write(longestConsecutive(root)); // This code is contributed by rag2127 </script>
Producción
3
Complejidad del tiempo: O (N) donde N es el número de nodos en un árbol binario determinado.
Espacio auxiliar: O(log(N))
También se analiza en el siguiente enlace:
Longitud máxima de ruta creciente consecutiva en árbol binario
