La clase java.io.LineNumberInputStream es simplemente una extensión del flujo de entrada que proporciona una función adicional para mantener el registro del número de línea actual.
Línea es una secuencia de bytes que termina con: 'r', es decir, un carácter de retorno de carro o un carácter de nueva línea: 'n' o un carácter de salto de línea que sigue al carácter de retorno de carro.
Declaración :
public class LineNumberInputStream extends Reader
Constructores:
LineNumberInputStream(InputStream in) : Constructs a newline no. stream that reads it's input from the specified Input Stream.
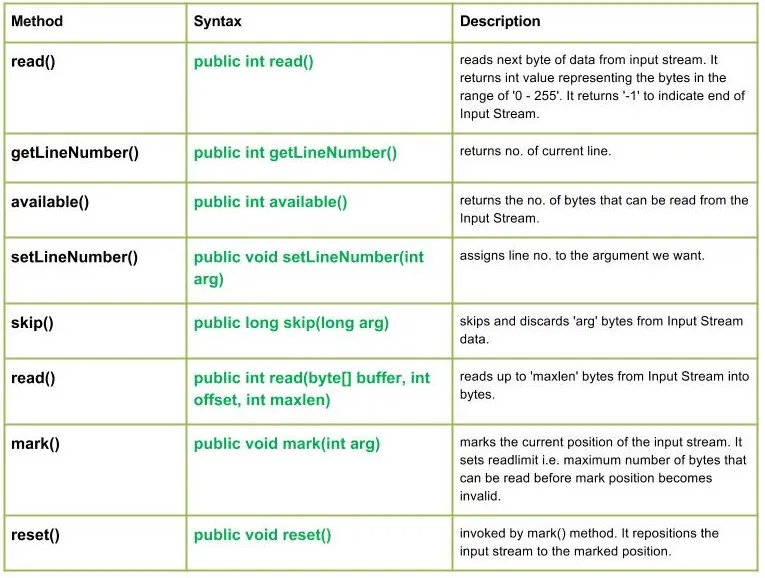
Métodos:
Sintaxis:
public int read() Parameters : ------- Return : int value representing the bytes in the range of '0 - 255'. return -1 indicating end of Input Stream. Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Implementación:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); // read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer // '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // Since read() method returns Integer value // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; System.out.print(c); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Nota :
El siguiente código Java no se ejecutará aquí porque no podemos acceder a ningún archivo en el IDE en línea.
Así que copie el programa a su sistema y ejecútelo allí.
El ABC.txt El archivo utilizado en el programa contiene:
Hello Geeks. Explaining read() method
Producción :
Hello Geeks. Explaining read() method
Sintaxis:
public int getLineNumber() Parameters : ------- Return : no. of current line
Implementación:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of getLineNumber() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try { char c; int a b; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // Use of getLineNumber() : to print line no. a = geekline.getLineNumber(); System.out.println(' At line : ' + a); System.out.print(c); } a = geekline.getLineNumber(); System.out.println(' at line: ' + a); } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Nota :
El siguiente código Java no se ejecutará aquí porque no podemos acceder a ningún archivo en el IDE en línea.
Así que copie el programa a su sistema y ejecútelo allí.
El ABC.txt El archivo utilizado en el programa contiene:
no. of lines
Producción :
At line : 0 n At line : 0 o At line : 0 . At line : 0 At line : 0 o At line : 0 f At line : 1 At line : 1 l At line : 1 i At line : 1 n At line : 1 e At line : 1 s at line: 1
Sintaxis:
public int available() Parameters : ------- Return : returns the no. of bytes that can be read from the Input Stream. Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Implementación:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of available() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a b; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // Use of available method : return no. of bytes that can be read a = geekline.available(); System.out.println(c + ' Bytes available : ' + a); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Nota :
El siguiente código Java no se ejecutará aquí porque no podemos acceder a ningún archivo en el IDE en línea.
Así que copie el programa a su sistema y ejecútelo allí.
El ABC.txt El archivo utilizado en el programa contiene:
available
Producción :
a Bytes available : 4 v Bytes available : 3 a Bytes available : 3 i Bytes available : 2 l Bytes available : 2 a Bytes available : 1 b Bytes available : 1 l Bytes available : 0 e Bytes available : 0
Sintaxis:
public void setLineNumber(int arg) Parameters : arg : line number to assign Return : void Exception: -----
Implementación:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of setLineNumber() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a b = 0; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // Use of setLineNumber() : to set the line no. geekline.setLineNumber(100 + b); // getLineNumber() : returning the current line no. a = geekline.getLineNumber(); System.out.println(c + ' Line No. Set : ' + a); b++; } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Nota :
El siguiente código Java no se ejecutará aquí porque no podemos acceder a ningún archivo en el IDE en línea.
Así que copie el programa a su sistema y ejecútelo allí.
El ABC.txt El archivo utilizado en el programa contiene:
LineNumber
Producción :
L Line No. Set : 100 i Line No. Set : 101 n Line No. Set : 102 e Line No. Set : 103 N Line No. Set : 104 u Line No. Set : 105 m Line No. Set : 106 b Line No. Set : 107 e Line No. Set : 108 r Line No. Set : 109
Sintaxis:
public long skip(long arg) Parameters : arg : no. of bytes of Input Stream data to skip. Return : no. of bytes to be skipped Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Implementación:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of setLineNumber() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a b = 0; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // skip() : to skip and discard 'arg' bytes // Here skip() will skip and discard 3 bytes. geekline.skip(3); System.out.println(c); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally{ // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Nota :
El siguiente código Java no se ejecutará aquí porque no podemos acceder a ningún archivo en el IDE en línea.
Así que copie el programa a su sistema y ejecútelo allí.
El ABC.txt El archivo utilizado en el programa contiene:
Program Explaining Skip() method
Producción : '
P r E a n k ) t
Sintaxis:
public int read(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) Parameters : buffer : buffer whose data to read offset : starting offset of the data maxlen : max. no. of bytes to read Return : total no. of bytes else return -1 if End of Input Stream is identified Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Implementación:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); // read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer // '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream while((a=geekline.read())!=-1) { // Since read() method returns Integer value // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; System.out.print(c); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Nota :
El siguiente código Java no se ejecutará aquí porque no podemos acceder a ningún archivo en el IDE en línea.
Así que copie el programa a su sistema y ejecútelo allí.
El ABC.txt El archivo utilizado en el programa contiene:
Read() method
lo que hace el método es offset = r y maxlen = 5... entonces ---es decir. 3 desplazamientos y luego 5 bytes, es decir, leer (luego nuevamente desplazarse, así que -
Producción :
The number of char read: 5 ---Read(--
Sintaxis:
public void mark(int arg) Parameters : arg : integer specifying the read limit of the input Stream Return : void
Sintaxis:
public void reset() Parameters : ---- Return : void Exception : -> IOException : If I/O error occurs.
Programa Java que explica los métodos de la clase LineNumberInputStream: reset() y mark()
gzip para linuxJava
// Java program illustrating the working of LineNumberInputStream method // mark() and reset() import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geek = null; try{ geek = new FileInputStream('GEEKS.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geek); // read() method : reading and printing Characters one by one System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); // mark() : read limiting the 'geek' input stream geekline.mark(0); // skip() : it results in reading of 'e' in G'e'eeks geekline.skip(1); System.out.println('skip() method comes to play'); System.out.println('mark() method comes to play'); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); boolean check = geekline.markSupported(); if(geekline.markSupported()) { // reset() method : repositioning the stream to marked positions. geekline.reset(); System.out.println('reset() invoked'); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); } else { System.out.println('reset() method not supported.'); } System.out.println('geekline.markSupported() supported reset() : ' + check); } catch(Exception except) { // in case of I/O error except.printStackTrace(); } finally { // releasing the resources back to the GarbageCollector when closes if(geek != null) geek.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Nota :
Este código no se ejecutará en el IDE en línea ya que dicho archivo no está presente aquí.
Puede ejecutar este código en su sistema para verificar el funcionamiento.
ABC.txt El archivo utilizado en el código tiene
HelloGeeks
Producción :
Char : H Char : e Char : l skip() method comes to play mark() method comes to play Char : o Char : G Char : e reset() method not supported. geekline.markSupported() supported reset() : false