Las listas son una de las estructuras de datos más utilizadas en Python. Seguimos usando listas en muchas aplicaciones diferentes, desde la resolución de problemas simples hasta problemas complejos. En Python, las listas reemplazan las matrices con ventajas como:
- Dinámico en tamaño
- Puede almacenar elementos de diferentes tipos de datos en una sola lista
Podemos acceder a los datos simplemente desde listas ordenadas; a diferencia de los conjuntos, los datos estarán desordenados. Para acceder a los datos, podemos utilizar varias formas de recorrer cada elemento dentro de una lista. Este tutorial cubre todas las formas con ejemplos.
1. Bucles
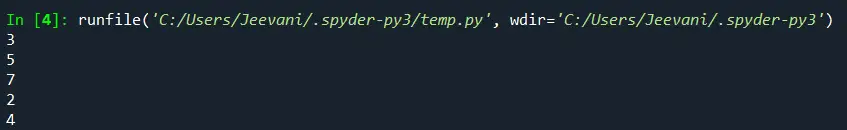
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] count = 0 while (count <len(list1)): 1 print (list1 [count]) count="count" + < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>We created a list with a few elements. Initially, count = 0. We're printing the element at the 'count' index and incrementing the count in the while loop. When the count reaches the length of the list, the loop will be terminated, and all the elements will already be accessed.</p> <p> <strong>Mechanism:</strong> </p> <table class="table"> <tr> <td>count = 0</td> <td>list1 [0]</td> <td>3</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 1</td> <td>list1 [1]</td> <td>5</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 2</td> <td>list1 [2]</td> <td>7</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 3</td> <td>list1 [3]</td> <td>2</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 4</td> <td>list1 [4]</td> <td>4</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 5 = len (list1)</td> <td>-</td> <td>-</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <tr><td>Using for loop:</td> </tr></ul> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] for i in list1: print (i) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-2.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>Using for-in, we accessed all the i's, the elements inside the list.</p> <ul> <tr><td>Using for and range:</td> </tr></ul> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] length = len (list1) for i in range (0, len (list1)): print (list1 [i]) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-3.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>The range function helps the 'for' loop to iterate from 0 to the given list's length.</p> <p> <strong>Mechanism:</strong> </p> <table class="table"> <tr> <td>the range gives - 0</td> <td>list1 [0]</td> <td>3</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 1</td> <td>list1 [1]</td> <td>5</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 2</td> <td>list1 [2]</td> <td>7</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 3</td> <td>list1 [3]</td> <td>2</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 4</td> <td>list1 [4]</td> <td>4</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <li>The range function doesn't give the last element specified - len (list1) = 5 is not given.</li> </ul> <h2>2. Using List Comprehension</h2> <p>This is the simple and suggested way to iterate through a list in Python.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] [print (i) for i in list1] print (' ') [print (list1 [i]) for i in range (0, len (list1))] print (' ') </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-4.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>We can use for loops inside a list comprehension. We used the same for loops we used in the above examples but inside a list in a single line. This way, we can reduce the length of the code and also list comprehension is a very subtle and efficient way to put loops in lists.</p> <h2>3. Using enumerate():</h2> <p>The enumerate function converts the given list into a list of tuples. Another important fact about this function is that it keeps count of the iterations. This is a built-in function in Python.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] for i, j in enumerate (list1): print ('index = ', i, 'value: ', j) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-5.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <h2>4. Using lambda function and map():</h2> <p>These are anonymous functions. There is a function map () in Python that can accept a function as an argument, and it calls the function with every element in the iterable, and a new list with all the elements from the iterable will be returned.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> list1 = [3, 6, 1, 8, 7] result = list (map (lambda num: num, list1)) print (result) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-6.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>The lambda num: num is given as an input to the map function along with the list. The function will take every single element in the list, accept it, and then return it. The map () function will pass the list elements one by one to the lambda function to return the elements.</p> <h2>What if we want to Iterate Multi-dimensional Lists?</h2> <p>There is an inbuilt module in Python designed to perform operations on multi-dimensional lists.</p> <p> <strong>1. To get numpy:</strong> </p> <p>Check if Python and pip are installed by opening the cmd via search and typing the commands:</p> <p> <strong>Python -version</strong> </p> <p> <strong>Pip --version</strong> </p> <p>If both Python and PIP are present in our system, it is now time to install our library:</p> <p> <strong>2. Open cmd from the start menu</strong> </p> <p> <strong>3. Type the command</strong> </p> <h3>pip install numpy</h3> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p>All the library packages, data, and sub-packages will be installed one after the other.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy list1 = numpy. arange (9) list1 = list1. reshape (3, 3) for x in numpy. nditer (list1): print (x) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-7.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>We imported the numpy module. Using the arrange method, we created an array with 9 elements. We accessed the list by reshaping it to 3 * 3 (rows * columns) using the reshape. Using the nditer function, we printed each element in the list.</p> <hr></len(list1)):>
Producción:

Comprensión:
Usando for-in, accedimos a todas las íes, los elementos dentro de la lista.
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] length = len (list1) for i in range (0, len (list1)): print (list1 [i])
Producción:

Comprensión:
La función de rango ayuda al bucle 'for' a iterar desde 0 hasta la longitud de la lista dada.
cuanto es 10 de 60
Mecanismo:
| el rango da - 0 | hoja1 [0] | 3 |
| el rango da - 1 | hoja1 [1] | 5 |
| el rango da - 2 | hoja1 [2] | 7 |
| el rango da - 3 | hoja1 [3] | 2 |
| el rango da - 4 | hoja1 [4] | 4 |
- La función de rango no proporciona el último elemento especificado: no se proporciona len (lista1) = 5.
2. Uso de la comprensión de listas
Esta es la forma sencilla y sugerida de recorrer una lista en Python.
Código:
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] [print (i) for i in list1] print (' ') [print (list1 [i]) for i in range (0, len (list1))] print (' ')
Producción:

Comprensión:
comentario multilínea de powershell
Podemos usar bucles for dentro de una lista por comprensión. Usamos los mismos bucles for que usamos en los ejemplos anteriores pero dentro de una lista en una sola línea. De esta manera, podemos reducir la longitud del código y también la comprensión de listas es una forma muy sutil y eficiente de colocar bucles en listas.
3. Usando enumerar():
La función enumerar convierte la lista dada en una lista de tuplas. Otro hecho importante de esta función es que lleva la cuenta de las iteraciones. Esta es una función incorporada en Python.
Código:
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] for i, j in enumerate (list1): print ('index = ', i, 'value: ', j)
Producción:

4. Usando la función lambda y map():
Estas son funciones anónimas. Hay un mapa de funciones () en Python que puede aceptar una función como argumento, llama a la función con cada elemento del iterable y se devolverá una nueva lista con todos los elementos del iterable.
Código:
list1 = [3, 6, 1, 8, 7] result = list (map (lambda num: num, list1)) print (result)
Producción:

Comprensión:
El lambda num: num se proporciona como entrada a la función de mapa junto con la lista. La función tomará cada elemento de la lista, lo aceptará y luego lo devolverá. La función map () pasará los elementos de la lista uno por uno a la función lambda para devolver los elementos.
¿Qué pasa si queremos iterar listas multidimensionales?
Hay un módulo incorporado en Python diseñado para realizar operaciones en listas multidimensionales.
1. Para volverse aturdido:
Compruebe si Python y pip están instalados abriendo el cmd mediante la búsqueda y escribiendo los comandos:
cadena un int
Versión de Python
Pip --versión
Si tanto Python como PIP están presentes en nuestro sistema, ahora es el momento de instalar nuestra biblioteca:
2. Abra cmd desde el menú inicio.
3. Escriba el comando
instalación de pip numpy
Todos los paquetes, datos y subpaquetes de la biblioteca se instalarán uno tras otro.
Código:
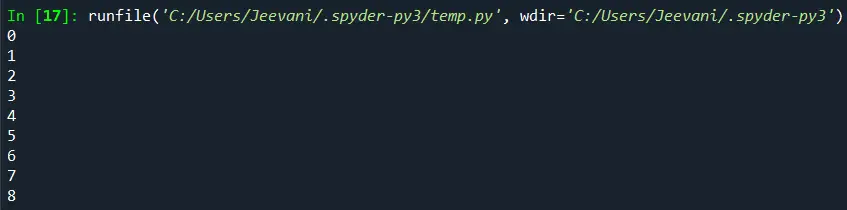
import numpy list1 = numpy. arange (9) list1 = list1. reshape (3, 3) for x in numpy. nditer (list1): print (x)
Producción:
Comprensión:
Importamos el módulo numpy. Usando el método de organización, creamos una matriz con 9 elementos. Accedimos a la lista remodelándola a 3 * 3 (filas * columnas) usando la remodelación. Usando la función nditer, imprimimos cada elemento de la lista.
