Este tutorial aprenderá cómo podemos aplicar un algoritmo de búsqueda binaria usando Python para encontrar la posición del índice de un elemento en la lista dada.
Introducción
Una búsqueda binaria es un algoritmo para encontrar un elemento particular en la lista. Supongamos que tenemos una lista de miles de elementos y necesitamos obtener una posición de índice de un elemento en particular. Podemos encontrar la posición del índice del elemento muy rápidamente utilizando el algoritmo de búsqueda binaria.
Existen muchos algoritmos de búsqueda, pero la búsqueda binaria es el más popular entre ellos.
Los elementos de la lista deben estar ordenados para aplicar el algoritmo de búsqueda binaria. Si los elementos no están ordenados, ordénelos primero.
Entendamos el concepto de búsqueda binaria.
Concepto de búsqueda binaria
En el algoritmo de búsqueda binaria, podemos encontrar la posición del elemento utilizando los siguientes métodos.
- Método recursivo
- Método iterativo
La técnica del enfoque de divide y vencerás es seguida por el método recursivo. En este método, una función se llama a sí misma una y otra vez hasta que encuentra un elemento en la lista.
Un conjunto de declaraciones se repite varias veces para encontrar la posición del índice de un elemento en el método iterativo. El mientras El bucle se utiliza para realizar esta tarea.
La búsqueda binaria es más efectiva que la búsqueda lineal porque no necesitamos buscar en cada índice de lista. La lista debe ordenarse para lograr el algoritmo de búsqueda binaria.
Veamos una implementación paso a paso de la búsqueda binaria.
Tenemos una lista ordenada de elementos y estamos buscando la posición del índice 45.
[12, 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54]
Entonces, estamos estableciendo dos consejos en nuestra lista. Se utiliza un puntero para indicar el valor más pequeño llamado bajo y el segundo puntero se utiliza para indicar el valor más alto llamado alto .
marquesina html
A continuación calculamos el valor de medio elemento en la matriz.
mid = (low+high)/2 Here, the low is 0 and the high is 7. mid = (0+7)/2 mid = 3 (Integer)
Ahora, compararemos el elemento buscado con el valor del índice medio. En este caso, 32 no es igual a 45. Entonces necesitamos hacer más comparaciones para encontrar el elemento.
Si el número que buscamos es igual a la mitad. Entonces regresa medio de lo contrario, pase a la comparación adicional.
El número a buscar es mayor que el medio número, comparamos el norte con el elemento central de los elementos en el lado derecho de medio y ponerlo bajo a bajo = medio + 1.
De lo contrario, compare el norte con el elemento medio de los elementos en el lado izquierdo de medio y establecer alto a alto = medio - 1.
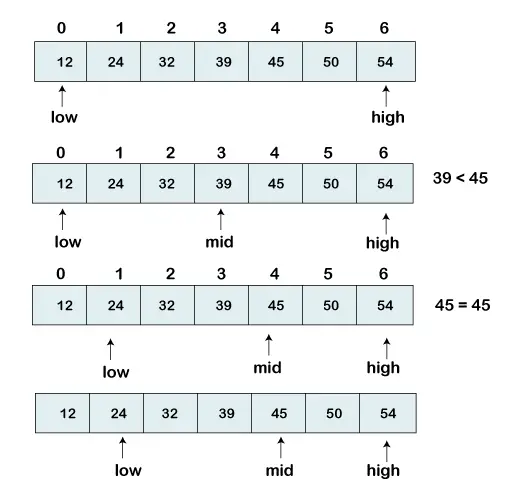
Repetir hasta encontrar el número que estamos buscando.
Implementar una búsqueda binaria en Python
Primero, implementamos una búsqueda binaria con el método iterativo. Repetiremos un conjunto de declaraciones e iteraremos cada elemento de la lista. Encontraremos el valor medio hasta completar la búsqueda.
Entendamos el siguiente programa del método iterativo.
Implementación de Python
# Iterative Binary Search Function method Python Implementation # It returns index of n in given list1 if present, # else returns -1 def binary_search(list1, n): low = 0 high = len(list1) - 1 mid = 0 while low <= 1 2 high: # for get integer result mid="(high" + low) check if n is present at list1[mid] n: high="mid" - smaller, compared to the left of else: return element was not in list, -1 initial list1 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54] function call n) !="-1:" print('element index', str(result)) list1') < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Element is present at index 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above program -</p> <ul> <li>We have created a function called <strong>binary_search()</strong> function which takes two arguments - a list to sorted and a number to be searched.</li> <li>We have declared two variables to store the lowest and highest values in the list. The low is assigned initial value to 0, <strong>high</strong> to <strong>len(list1)</strong> - 1 and mid as 0.</li> <li>Next, we have declared the <strong>while</strong> loop with the condition that the <strong>lowest</strong> is equal and smaller than the <strong>highest</strong> The while loop will iterate if the number has not been found yet.</li> <li>In the while loop, we find the mid value and compare the index value to the number we are searching for.</li> <li>If the value of the mid-index is smaller than <strong>n</strong> , we increase the mid value by 1 and assign it to The search moves to the left side.</li> <li>Otherwise, decrease the mid value and assign it to the <strong>high</strong> . The search moves to the right side.</li> <li>If the n is equal to the mid value then return <strong>mid</strong> .</li> <li>This will happen until the <strong>low</strong> is equal and smaller than the <strong>high</strong> .</li> <li>If we reach at the end of the function, then the element is not present in the list. We return -1 to the calling function.</li> </ul> <p>Let's understand the recursive method of binary search.</p> <h2>Recursive Binary Search</h2> <p>The recursion method can be used in the binary search. In this, we will define a recursive function that keeps calling itself until it meets the condition.</p> <p>Let's understand the above program using the recursive function.</p> <h3>Python Program</h3> <pre> # Python program for recursive binary search. # Returns index position of n in list1 if present, otherwise -1 def binary_search(list1, low, high, n): # Check base case for the recursive function if low n: return binary_search(list1, low, mid - 1, n) # Else the search moves to the right sublist1 else: return binary_search(list1, mid + 1, high, n) else: # Element is not available in the list1 return -1 # Test list1ay list1 = [12, 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54] n = 32 # Function call res = binary_search(list1, 0, len(list1)-1, n) if res != -1: print('Element is present at index', str(res)) else: print('Element is not present in list1') </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Element is present at index 2 </pre> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> </p> <p>The above program is similar to the previous program. We declared a recursive function and its base condition. The condition is the lowest value is smaller or equal to the highest value.</p> <ul> <li>We calculate the middle number as in the last program.</li> <li>We have used the <strong>if</strong> statement to proceed with the binary search.</li> <li>If the middle value equal to the number that we are looking for, the middle value is returned.</li> <li>If the middle value is less than the value, we are looking then our recursive function <strong>binary_search()</strong> again and increase the mid value by one and assign to low.</li> <li>If the middle value is greater than the value we are looking then our recursive function <strong>binary_search()</strong> again and decrease the mid value by one and assign it to low.</li> </ul> <p>In the last part, we have written our main program. It is the same as the previous program, but the only difference is that we have passed two parameters in the <strong>binary_search()</strong> function.</p> <p>This is because we can't assign the initial values to the low, high and mid in the recursive function. Every time the recursive is called the value will be reset for those variables. That will give the wrong result.</p> <h2>Complexity</h2> <p>The complexity of the binary search algorithm is <strong>O(1)</strong> for the best case. This happen if the element that element we are looking find in the first comparison. The <strong>O(logn)</strong> is the worst and the average case complexity of the binary search. This depends upon the number of searches are conducted to find the element that we are looking for.</p> <h2>Conclusion</h2> <p>A binary search algorithm is the most efficient and fast way to search an element in the list. It skips the unnecessary comparison. As the name suggests, the search is divided into two parts. It focuses on the side of list, which is close to the number that we are searching.</p> <p>We have discussed both methods to find the index position of the given number.</p> <hr></=> Explicación:
En el programa anterior -
- Hemos creado una función llamada búsqueda binaria() función que toma dos argumentos: una lista para ordenar y un número para buscar.
- Hemos declarado dos variables para almacenar los valores más bajos y más altos de la lista. Al mínimo se le asigna un valor inicial de 0, alto a len(lista1) - 1 y medio como 0.
- A continuación hemos declarado la mientras bucle con la condición de que el más bajo es igual y menor que el más alto El bucle while se repetirá si aún no se ha encontrado el número.
- En el ciclo while, encontramos el valor medio y comparamos el valor del índice con el número que estamos buscando.
- Si el valor del índice medio es menor que norte , aumentamos el valor medio en 1 y lo asignamos a La búsqueda se mueve hacia el lado izquierdo.
- De lo contrario, disminuya el valor medio y asígnelo al alto . La búsqueda se desplaza hacia el lado derecho.
- Si n es igual al valor medio, entonces devuelve medio .
- Esto sucederá hasta el bajo es igual y menor que el alto .
- Si llegamos al final de la función, entonces el elemento no está presente en la lista. Devolvemos -1 a la función de llamada.
Entendamos el método recursivo de búsqueda binaria.
Búsqueda binaria recursiva
El método de recursividad se puede utilizar en la búsqueda binaria. En esto, definiremos una función recursiva que sigue llamándose a sí misma hasta que cumple la condición.
valor java de la cadena
Entendamos el programa anterior usando la función recursiva.
Programa Python
# Python program for recursive binary search. # Returns index position of n in list1 if present, otherwise -1 def binary_search(list1, low, high, n): # Check base case for the recursive function if low n: return binary_search(list1, low, mid - 1, n) # Else the search moves to the right sublist1 else: return binary_search(list1, mid + 1, high, n) else: # Element is not available in the list1 return -1 # Test list1ay list1 = [12, 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54] n = 32 # Function call res = binary_search(list1, 0, len(list1)-1, n) if res != -1: print('Element is present at index', str(res)) else: print('Element is not present in list1')
Producción:
Element is present at index 2
Explicación
El programa anterior es similar al programa anterior. Declaramos una función recursiva y su condición base. La condición es que el valor más bajo sea menor o igual al valor más alto.
- Calculamos el número del medio como en el último programa.
- Hemos utilizado el si declaración para continuar con la búsqueda binaria.
- Si el valor medio es igual al número que estamos buscando, se devuelve el valor medio.
- Si el valor medio es menor que el valor, entonces estamos buscando nuestra función recursiva búsqueda binaria() nuevamente y aumente el valor medio en uno y asígnelo a bajo.
- Si el valor medio es mayor que el valor que estamos buscando, entonces nuestra función recursiva búsqueda binaria() nuevamente y disminuya el valor medio en uno y asígnelo a bajo.
En la última parte, hemos escrito nuestro programa principal. Es igual que el programa anterior, pero la única diferencia es que le hemos pasado dos parámetros en el búsqueda binaria() función.
Esto se debe a que no podemos asignar los valores iniciales a bajo, alto y medio en la función recursiva. Cada vez que se llama al recursivo, el valor se restablecerá para esas variables. Eso dará un resultado incorrecto.
Complejidad
La complejidad del algoritmo de búsqueda binaria es O(1) para el mejor de los casos. Esto sucede si el elemento que estamos buscando lo encontramos en la primera comparación. El O(iniciar sesión) es el peor y el caso de complejidad promedio de la búsqueda binaria. Esto depende del número de búsquedas que se realicen para encontrar el elemento que buscamos.
Conclusión
Un algoritmo de búsqueda binaria es la forma más eficiente y rápida de buscar un elemento en la lista. Se salta la comparación innecesaria. Como sugiere el nombre, la búsqueda se divide en dos partes. Se centra en el lado de la lista, que está cerca del número que estamos buscando.
Hemos discutido ambos métodos para encontrar la posición del índice del número dado.
